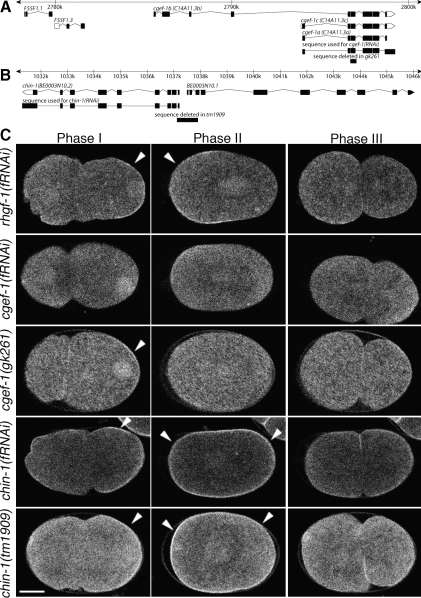
Figure 3.
Wild-type CDC-42 activity requires the putative GEF CGEF-1 and the putative GAP CHIN-1. (A) Physical map of the portion of the C. elegans genome including predicted cgef-1–related ORFs, region deleted in the gk261 mutation, and the target sequence used for cgef-1(RNAi). (B) Physical map of the portion of the C. elegans genome including the predicted chin-1 and BE0003N10.1 ORFs, region deleted in the tm1909 mutation, and the target sequence used for chin-1(RNAi). (C) GFP::GBDwsp-1 localization in embryos during phases I, II, and III. Embryos from mothers treated with RNAi directed toward the RhoGEF-encoding rhgf-1, cgef-1, or chin-1. Specificity of RNAi target was tested by comparing the RNAi phenotype to the phenotype of embryos from cgef-1(gk261) or chin-1(tm1909) mothers. Note the persistence of nuclear signal in cgef-1(gk261) embryos. Arrowheads indicate polarized enrichment of cortical signal. Bar, 10 μm.