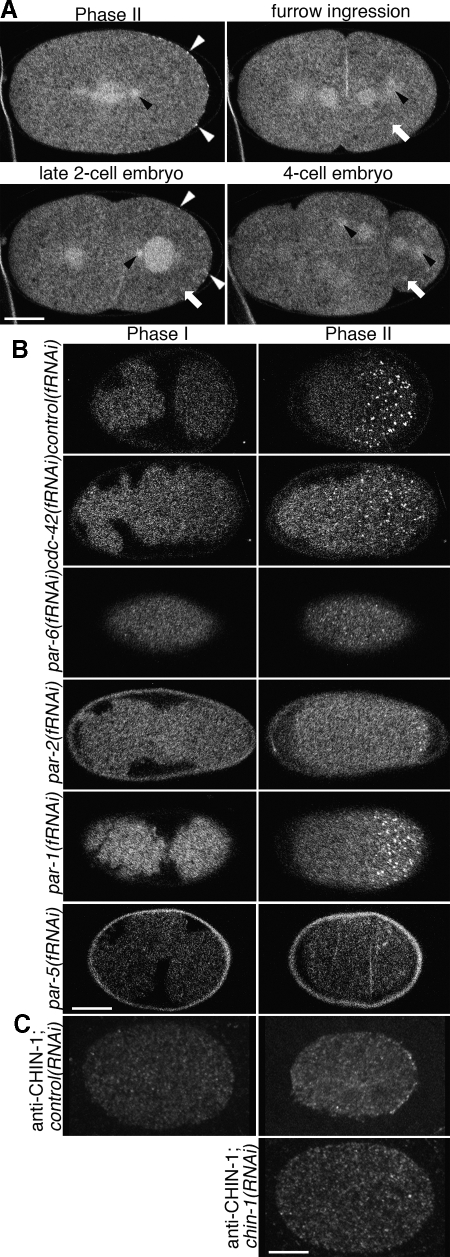
Figure 5.
Localization of GFP::CHIN-1 depends on CDC-42, PAR-6 and PAR-2 but not PAR-1. Embryos expressing GFP::CHIN-1 in the early embryo. (A) Optical sections through the middle of the cell. GFP::CHIN-1 localizes to the cytoplasm, centrosomes (black arrowheads), central spindle, cortical puncta (white arrowheads) and some structures suggestive of P-granules (white arrows). The cortical puncta are only observed in the early embryo at the posterior during phase II and at the posterior during the late two-cell stage. (B) Optical sections through the cortex of the cell. Cortical localization depends upon some polarity proteins. Embryos depleted of CDC-42 or PAR-6 exhibit puncta all about the cortex in phase II. Embryos depleted of PAR-2 exhibit cortical puncta only at the extreme posterior, whereas those depleted of PAR-1 exhibit only a slight reduction of the posterior domain that contains puncta. No depletion altered the absence of puncta in phase I. Embryos depleted of PAR-5 exhibited a dramatic reduction in GFP::CHIN-1 signal and an absence of cortical puncta. (C) Optical sections through the middle of the cell. Anti-CHIN-1 antibody localizes as posterior cortical puncta during phase II. This localization is lost in chin-1(RNAi) embryos. Bar, 10 μm.