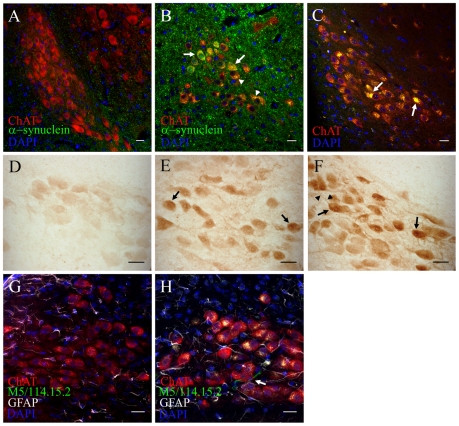
Figure 3. Intragastrically administered rotenone induces alpha-synuclein accumulation, oxidative stress and inflammation in the dorsal motor nucleus vagus.
(scale bars 20 µm). A, B, double-immunofluorescence staining against alpha-synuclein and ChAT on DMV sections from 1.5 months control (A) and 1.5 months treated (B) mice. Arrows in B, increased intracellular alpha-synuclein in DMV neurons already after 1.5 months. Arrowheads in B, autofluorescent punctate inclusion pattern inside ChAT+ neurons. C, DMV sections stained with ChAT and DAPI were sequentially excited with 488 and 561 laser wavelengths. Arrows in C, large intracellular auto-fluorescent inclusions inside ChAT+ neurons of the DMV (arrows). D, E, F, Light microscopy images of alpha-synuclein staining from 1.5 months control (D), 1.5 months (E) and 3 months (F) treated mice. Arrows in E and F, increased staining intensity inside DMV neuronal soma in treated mice. Arrowheads in F, increased alpha-synuclein staining inside neuronal processes G, H, average-projection of triple-immunofluorescence staining against ChAT, GFAP, MHC II (clone M5/114.15.2) and DAPI on sections from control (G) and treated (H) mice after 3 month treatment. Arrow in H, activated microglial cell in the DMV.