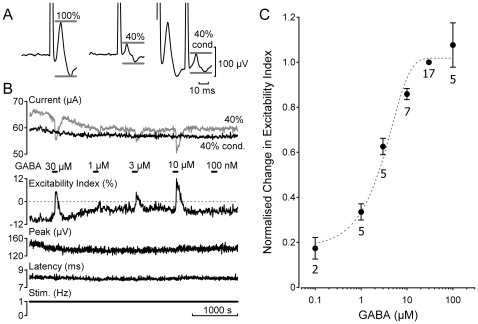
Figure 1. GABA activation of human C-fibres is concentration dependent.
The excitability index was determined for C-fibres in human sural nerve fascicles during bath application of GABA (0.1–100 µM). A time window restricted the domain over which the amplitude of the electrically-evoked compound C-fibre action potential was determined (A, grey bars). Excitability index was calculated from the ratio of the current required to evoke an unconditioned C-fibre response of 40% maximum amplitude to that required to evoke a conditioned 40% response, i.e. 30 ms after a supra-maximal conditioning stimulus (40% cond., grey). Negative values of excitability index indicate that more current is required to evoke an unconditioned 40% C-fibre response. Following the addition of GABA (0.1–30 µM, 90 s application) to the bathing solution the excitability index increases, i.e. becomes more positive (B), and the magnitude of this change increases as the concentration of GABA in the perfusing solution increases (B & C). The EC50 determined from a sigmoid fit to normalised excitability index on GABA concentration was 6.88±0.01 µM.