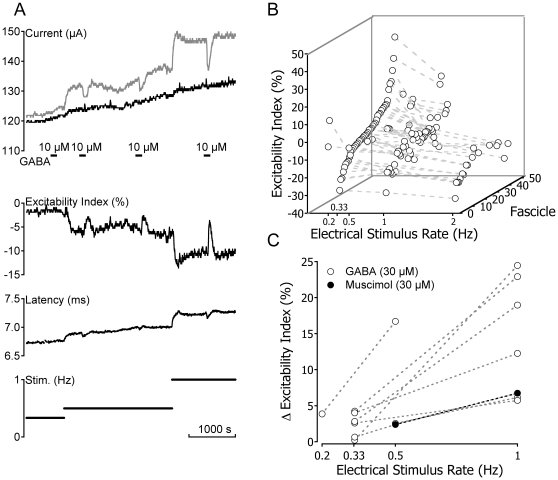
Figure 3. Higher rates of electrical stimulation render human C-fibres less excitable but enhance responses to GABA.
The magnitude of the excitability index increase in response to GABA increases with the rate of electrical stimulation. An increase in the rate of electrical stimulation reduces the excitability index of C-fibres (A & B). The absolute magnitude of stimulus rate-induced decreases in excitability index varies (B). The reduction in excitability index produced by increased electrical stimulation rate always increases the magnitude of the change in excitability index observed in response to bath application of GABA or muscimol (10–30 µM, A & C).