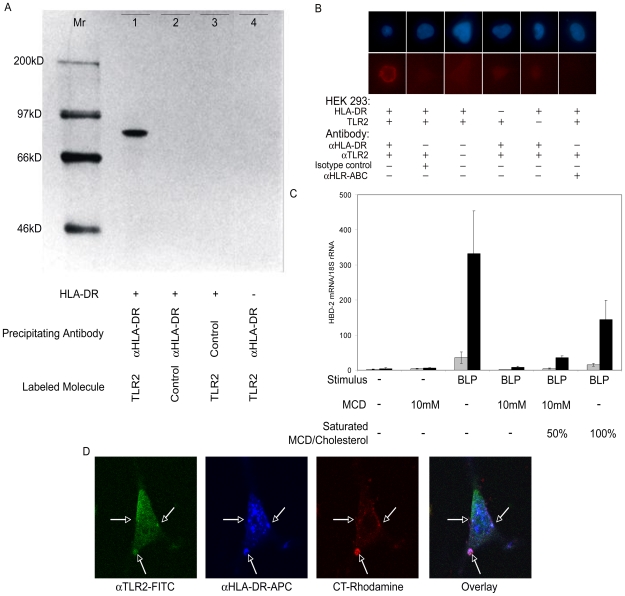
Figure 3. TLR2 and HLA-DR interact physically in lipid raft domains.
(A) Co-precipitation of labeled recombinant TLR2 (lane 1, 3, 4) or a control protein (lane 2, luciferase) with HLA-DR molecules purified by immunoprecipitation with anti HLA-DR antibodies (lane 1, 2, 4) or control antibodies (lane 3) from cell lysates of HLA-DR positive (lane 1, 2, 3) or negative (lane 4) HEK293 cells. A 14C-labeled molecular weight marker (in kD) is shown in the left lane. (B) Proximity ligation assays showed that TLR2 and HLA-DR are close together (red signal), while TLR2 and HLA-ABC do not co-localize (no red signal). Nuclei are stained by Hoechst 33342 (blue). (C) Treatment of TLR2+ (grey bars; n = 3) or HLA-DR+/TLR2+ (black bars; n = 3) HEK293 cells with MCD, a lipid raft-destroying agent, prior to stimulation with BLP leads to impaired hBD-2 gene expression. The effect is restored via adding MCD saturated with cholesterol acting as cholesterol donor. Error bars represent standard errors. (D) Immunofluorescence microscopy showed that TLR2 (αTLR2-FITC; green) and HLA-DR (αHLA-DR-APC-Cy9; blue) co-localize in lipid raft domains (CT-rhodamine; red) of HLA-DR+/TLR2+ HEK293 cells (indicated by the white arrows). Pictures are representatives of at least five experiments.