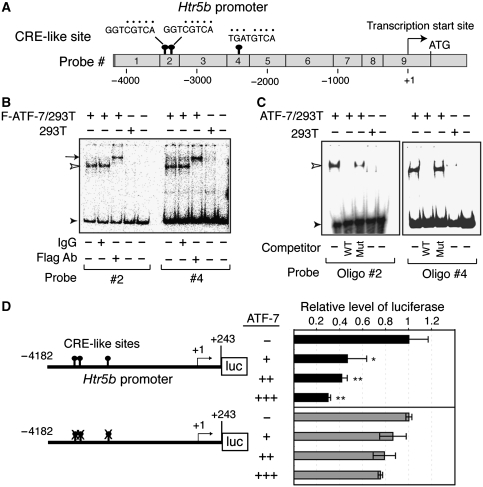
Figure 3.
Binding of ATF-7 to the 5-HT receptor 5B (Htr5b) promoter region leads to silencing. (A) Presence of cAMP response element (CRE)-like sites in the 5′ region of the mouse Htr5b gene. The CRE-like sites in the 5′-region of mouse Htr5b, and nine DNA probes used for gel mobility-shift assays are shown. (B, C) Gel mobility-shift assays were performed using nuclear extracts prepared from 293T cells transfected with a Flag-ATF-7 expression vector or control empty vector. The #2 and #4 DNA probes were used as the probes in (B). In some lanes, anti-Flag or control IgG was added. In (C), oligonucleotides containing the two CRE-like sites derived from probe #2 or the one CRE-like site from probe #4 were used as probes. In some lanes, a 50-fold excess of competitor containing the same sequence as the probe (wild-type (WT)), or a mutated CRE-like site, was added. Free probe is indicated by a closed arrowhead, whereas ATF-7-bound DNA is shown by an open arrowhead. The ATF-7-DNA complex, which was super-shifted by the anti-Flag antibody, is indicated by the arrow. (D) ATF-7 represses Htr5b gene transcription. RN46A cells were transfected with the indicated Htr5b promoter-luciferase construct together with 1 (+), 2 (++), or 3 (+++) μg of the ATF-7 expression plasmid, or the control empty vector (−), and luciferase activity was measured. Values indicate mean±s.d. (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.