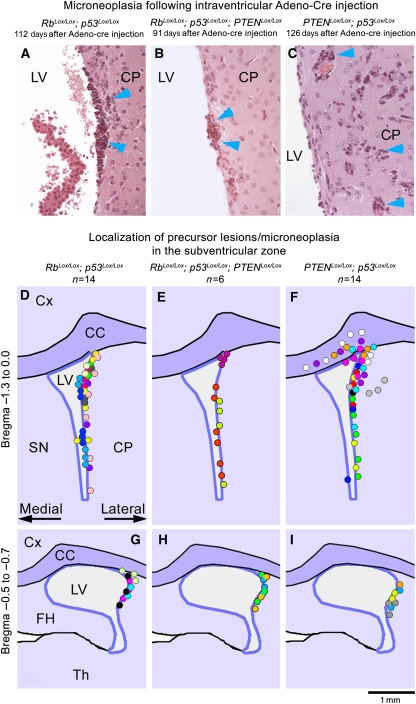
Figure 4.
Small neoplastic lesions (‘microneoplasia') after intraventricular Adeno-cre injection precede brain tumours. Upper row (A–C): Histological appearance of small neoplastic lesions located beneath the ependymal layer of the lateral wall of the ventricle. Occasionally, perivascular spread was seen in PTEN/p53 mice (C). (D–I) Schematic representation of precursor lesions: cumulative maps showing the localization of small lesions. Each dot represents microneoplasia or a focal cluster of tumour cells (approximately 200 μm). Each colour represents an individual animal. The map summarizes lesions in 14 Rb/p53 mice, 6 Rb/p53/PTEN mice and 14 PTEN/p53 mice. The upper schematic panel (D–F) summarizes lesions in the anterior ventricular region (Bregma −1.3 to 0.0) and the lower panel (G–I) represents the posterior region (Bregma −0.5 to −0.7). The microneoplastic lesions are almost exclusively localized beneath the lateral wall of the ventricles and in the lateral corner of the ventricle, and may occasionally protrude to the opposite wall. Although Rb/p53 and Rb/p53/PTEN lesions tend to remain locally clustered, PTEN/p53 lesions often spread laterally and into the corpus callosum, in keeping with the more infiltrative nature of these tumours (F). One small lesion in an Rb/p53 animal (D, yellow dot) was observed extending to the medial side but may not have arisen there and one small lesion in a PTEN/p53 animal arose from the medial surface (F, blue dot), indicating a very strong preference for the lateral/dorsolateral walls, consistent with the presumed localization of SVZ stem cells. Cx, cortex; CC, corpus callosum; LV, lateral ventricle; SN, septal nuclei; FH, fimbria hippocampi and Th, thalamus.