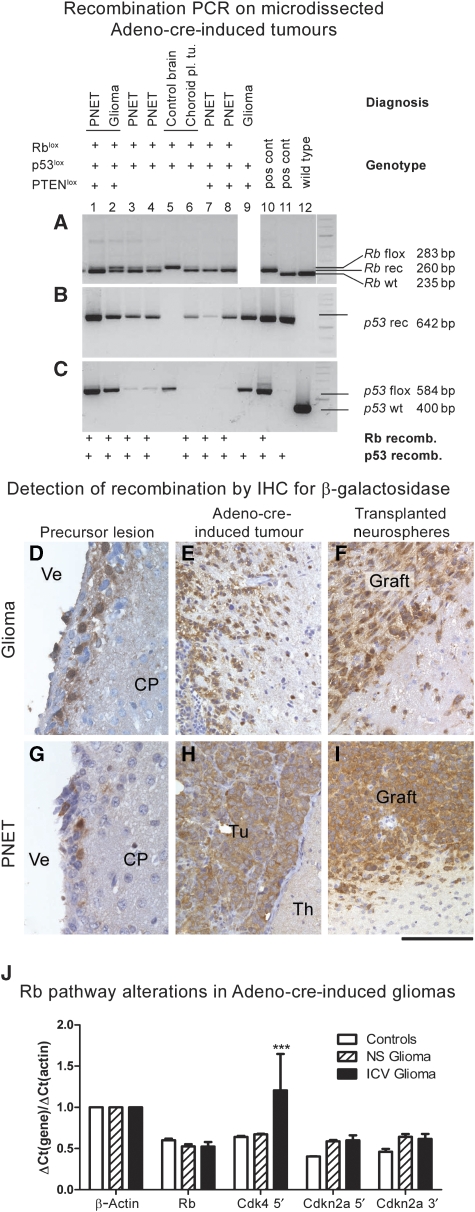
Figure 5.
Gene recombination in experimentally induced brain tumours: (A–C) recombination PCR on microdissected tumours demonstrates recombination of floxed genes in brain tumours: Lanes 1 and 2: rare instance of two histologically distinct tumour phenotypes in the same brain (mouse genotype Rb/p53), both showing recombination of Rb (A) and p53 (B, C). Lanes 3, 4, 7 and 8 are further examples of recombination in PNETs, whereas lane 6 shows recombination in other tumour types and no recombination is seen in control tissue. Lane 8 shows glioma with recombination of p53. PTEN recombination was not tested in these tumours. (D–I): Immunohistochemical detection of β-galactosidase in recombined cells of precursor lesions (D, G), Adeno-cre-induced primary brain tumours (E, H) and in tumours derived from grafted neurospheres that were recombined in vitro before implantation (F, I). As all mice carried the ROSA26lox gene, recombination results in β-galactosidase expression in recombined SVZ cells, microneoplasia and tumours but not in uninfected brain parenchyma. Ve, ventricle; CP, caudoputamen; Tu, tumour, Th, thalamus. Scale bar: 60 μm (D, G); 120 μm (E, F, H, I). (J) Expression analysis of the Rb pathway in primary tumours (solid bars) and grafts (shaded bars). RNA extracted from two normal forebrains served as controls (white bars). Gene transcripts: Rb, Cdk4, Cdkn2a 5′ (p16/Ink4a and p19/Arf), Cdkn2a 3′ (p19/Arf) and β-actin. The 5′ transcript of Cdk4 is significantly (P<0.001) upregulated in brain tumours, whereas there is a statistically non-significant upregulation of p16/Ink4a and p19/Arf transcripts.