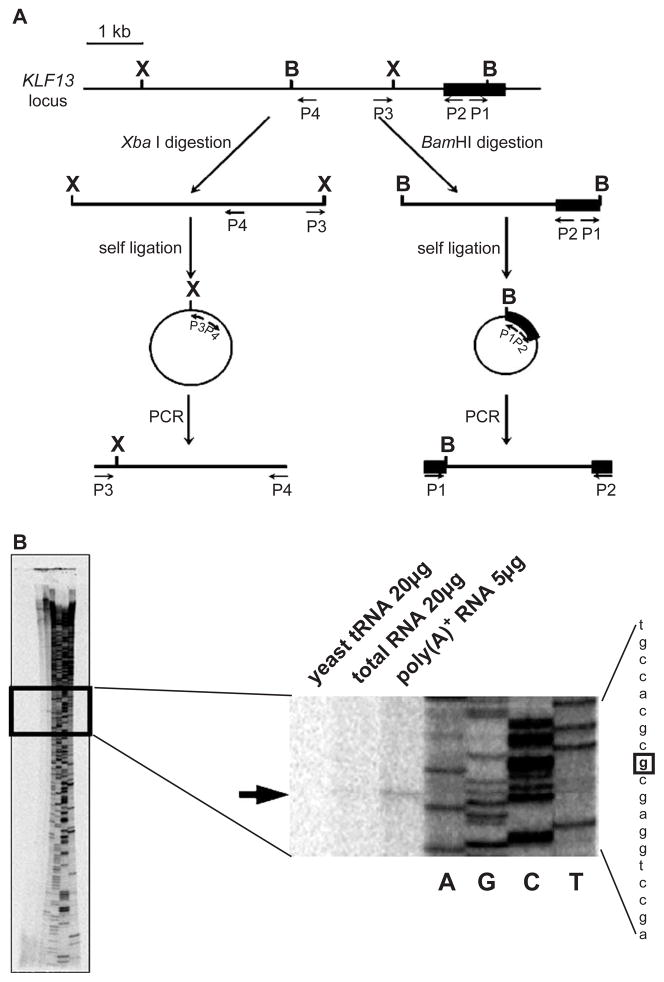
Fig. 1.
Promoter of the KLF13 gene. (A) Cloning of the 5′ flanking region of KLF13 gene by inverse PCRs. The first exon is shown by a solid rectangle. B and X represent the BamHI and XbaI sites, respectively. Primers used in inverse PCRs are indicated by arrows (P1–P4). Note that the positions of upstream BamHI and XbaI sites are unknown prior to the experiments. (B) Primer extension analysis of KLF13 mRNA. RNAs used in the analysis are indicated above. Products of the sequencing reaction using the same probe were run on gel together, of which reading is shown at right. An arrow indicates the position of the extension product. The nucleotide in the sequence is highlighted by a square.