Table 1.
Conformational tuning of properties of antimicrobial oligomersa.
| Compound | Structure | MIC (μM) S. aureusb |
E. Coli D31 |
HC50 (μM)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 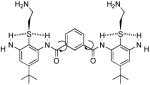 |
50 | 12.5 | 14 |
| 3 | 7.8 | 3.9 | 445 | |
| 4 | 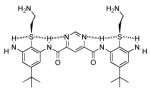 |
0.80 | 0.80 | 18 |
| 5 | 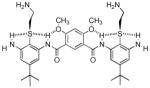 |
0.87 | 0.87 | 145 |
| 6 | 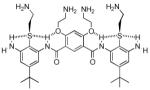 |
0.66 | 5.3 | 593 |
| 7 | 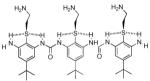 |
0.70c | 0.70 | 5 |
| 8 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 63-90 | |
| 9 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 40 | |
| 10 | 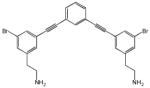 |
0.20 | 0.10 | 440 |
Data were collected using the Hancock method; numbers quoted here may differ somewhat from those in the original publications if a different method was originally used to determine MIC’s.
Tetracycline and streptomycin-resistant S. aureus.
The concentration required to cause 50% lysis of a suspension of red blood cells.
