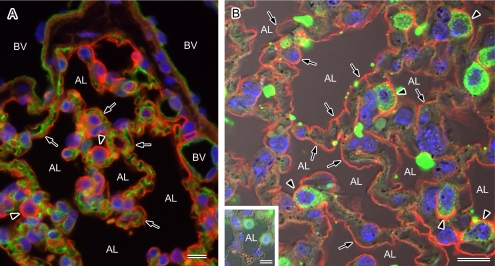
Fig. 5.
Localization of AQP1 and AQP5 in the mouse alveoli. Paraffin sections of the mouse lung were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy after antigen retrieval for the localization of AQP1 and AQP5. Nuclear DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). A: Double staining for AQP1 (green) and AQP5 (red) observed under a low magnification with a conventional microscope. AQP1 and AQP5 staining can be seen on the vascular side and at the alveolar surface (arrows), respectively. The entire alveolar surface is positive for AQP5 and strong expression of this isoform can be seen in the protruding cells (arrowheads). BV, blood vessel; AL, alveolar lumen. B: Double staining for AQP5 (red) and the type II cell marker SP-A (green) observed under high magnification with a laser confocal microscope. A fluorescent image merged with a corresponding Nomarski image is shown. The entire luminal surface is positive for AQP5 (arrows) and stronger signals for this isoform are evident at the apical membranes of SP-A-positive type II alveolar cells (arrowheads). Positive labeling for AQP5 is abolished in the presence of the antigen peptide (inset). AL, alveolar lumen. Bars=10 µm.