Fig. 3.
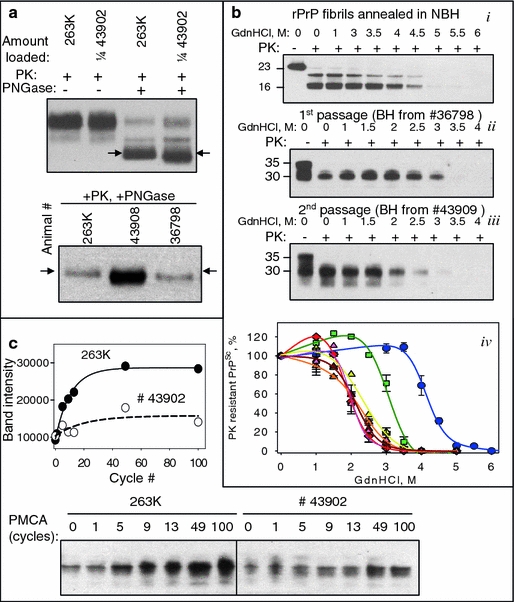
Biochemical characterization of the de novo generated prions. a BHs from the first (animal #36798) or second passage (animals #43902 and #43908) of NBH-annealed fibrils were treated with PK and PNGase and analyzed by Western blotting. Arrows indicate the center of the deglycosylated PrPSc from 263K-inoculated hamsters. BH #43902 was loaded at 1/4th of the amount of 263K BH. b Western blotting and the conformational stability profiles (iv) of the GdnHCl-induced transitions of the NBH-annealed fibrils (i), or PrPSc from first (ii) or second (iii) passage of NBH-annealed fibrils. NBH-annealed fibrils (blue circles), PrPSc from first passage (green square, animal #36798), second passage (yellow, orange, brown, or pink triangles—animals #43902, 43904, 43908, or 43909), or 263K-inoculated animals (red diamonds). Each BH was loaded onto the gel twice and the data were averaged. c The amplification kinetics for 263K or PrPSc from second passage of NBH-annealed fibrils (BH #43902) as monitored by Western blotting during a single round of PMCA that consisted of 100 cycles. Samples in a, b (ii and iii) were treated with 20 μg/ml PK; samples in c with 50 μg/ml PK; and samples in b (i) with 2 μg/ml PK
