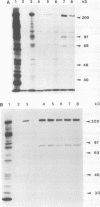
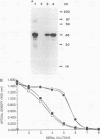
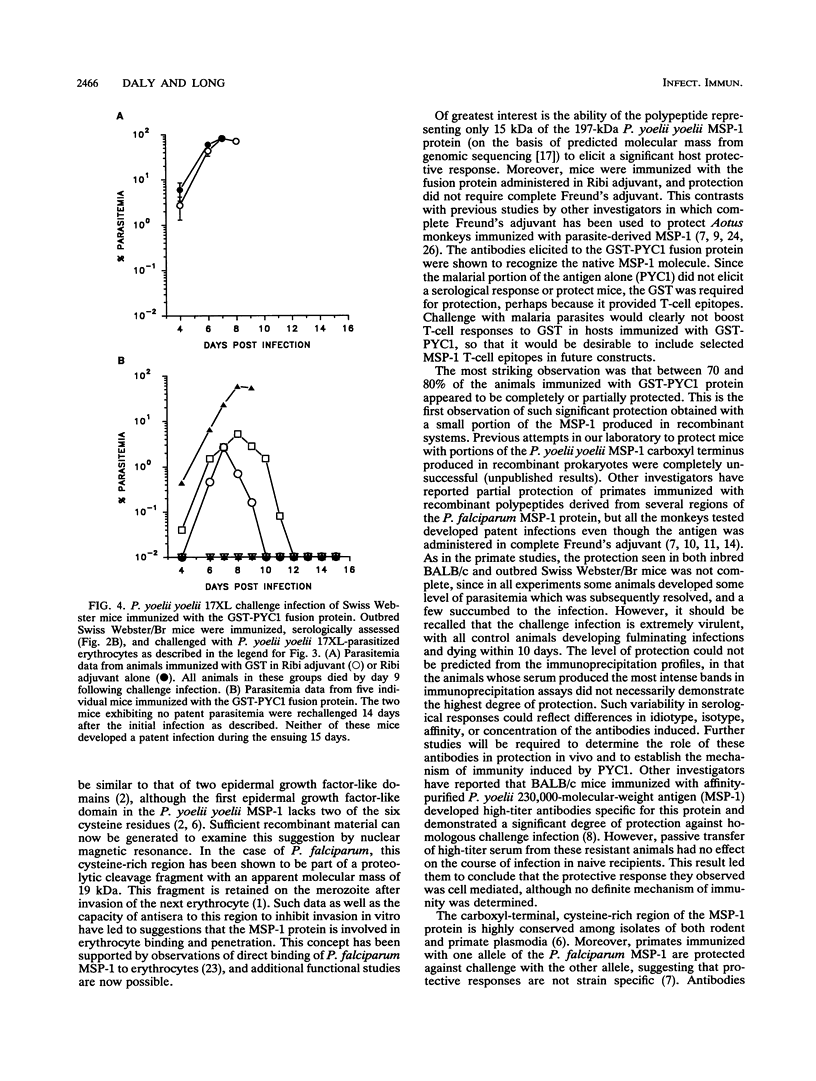
Abstract
Since the developmental stages of malarial parasites which replicate within erythrocytes are responsible for the morbidity and mortality associated with this disease, antigens produced by these stages have been proposed as candidates for a vaccine. One surface protein of merozoites (MSP-1) has been shown to immunize both rodents and primates against virulent challenge infection in experimental systems. However, little is known of relevant epitopes on the molecule, and attempts to obtain recombinant MSP-1 polypeptides in a native configuration have proven difficult. We have found that the cysteine-rich, carboxyl-terminal region of the MSP-1 protein from the rodent malarial parasite Plasmodium yoelii yoelii can be expressed in a native configuration as a fusion protein in Escherichia coli. This recombinant polypeptide containing 15 kDa of the predicted 197-kDa protein elicits antibodies in mice which recognize the native parasite MSP-1. Most significantly, both inbred and outbred mice immunized with the fusion protein in Ribi adjuvant are partially and in some cases completely protected against challenge infection with an otherwise lethal parasite strain. This is the first observation of such significant protection obtained with a small portion of the MSP-1 produced in recombinant systems.
Full text
PDF

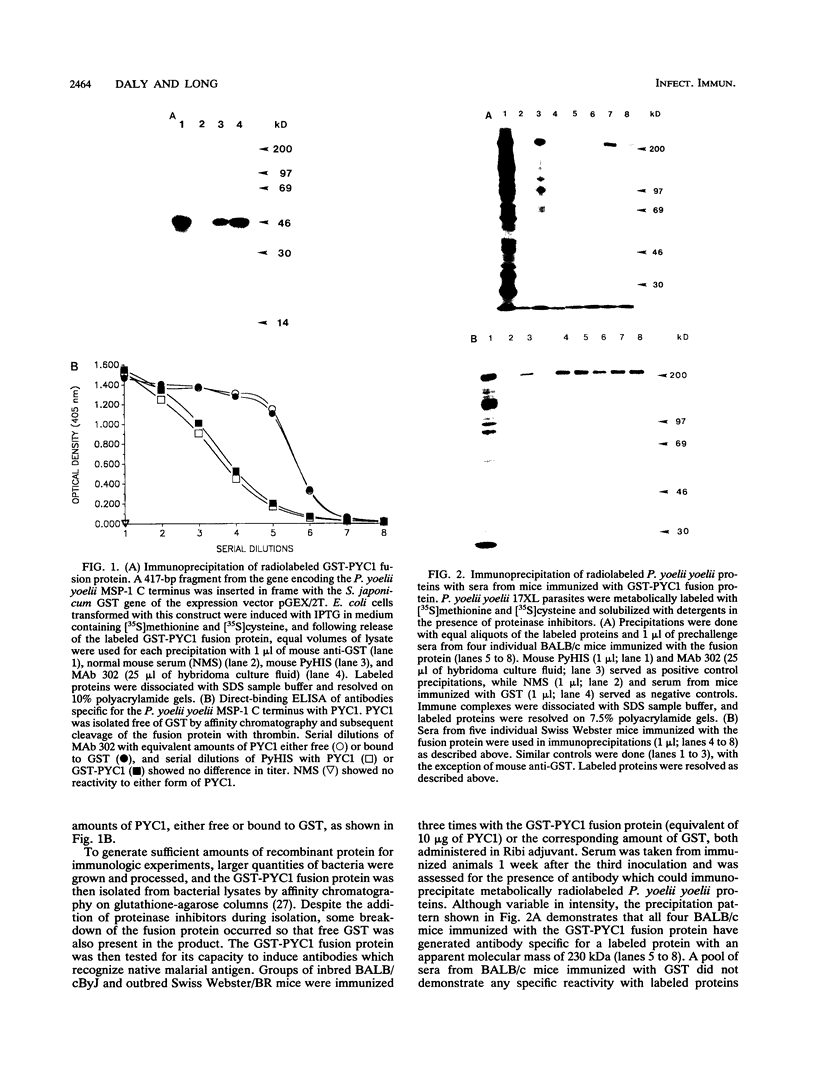
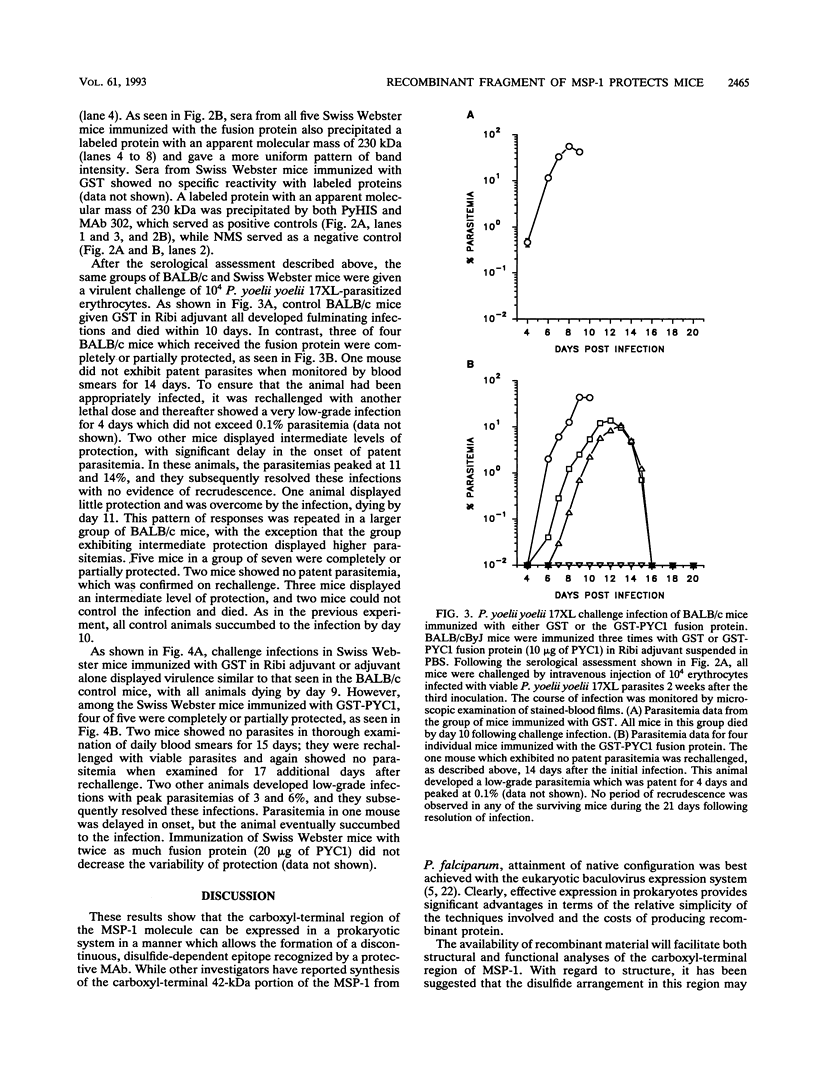

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. J., Heidrich H. G., Donachie S., McBride J. S., Holder A. A. A single fragment of a malaria merozoite surface protein remains on the parasite during red cell invasion and is the target of invasion-inhibiting antibodies. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):379–382. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M. J., Ling I. T., Nicholls S. C., Holder A. A. Proteolytic processing of the Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein-1 produces a membrane-bound fragment containing two epidermal growth factor-like domains. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90127-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. M., Jr, Daly T. M., Vaidya A. B., Long C. A. The 3' portion of the gene for a Plasmodium yoelii merozoite surface antigen encodes the epitope recognized by a protective monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. M., Jr, Majarian W. R., Young J. F., Daly T. M., Long C. A. A protective monoclonal antibody recognizes an epitope in the carboxyl-terminal cysteine-rich domain in the precursor of the major merozoite surface antigen of the rodent malarial parasite, Plasmodium yoelii. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2670–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. P., Gibson H. L., Lee-Ng C. T., Barr P. J., Hui G. S. A carboxyl-terminal fragment of Plasmodium falciparum gp195 expressed by a recombinant baculovirus induces antibodies that completely inhibit parasite growth. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. M., Burns J. M., Jr, Long C. A. Comparison of the carboxy-terminal, cysteine-rich domain of the merozoite surface protein-1 from several strains of Plasmodium yoelii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jun;52(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90061-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger H. M., Caspers P., Matile H., Schoenfeld H. J., Stueber D., Takacs B. Ability of recombinant or native proteins to protect monkeys against heterologous challenge with Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3498–3503. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3498-3503.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. R., Holder A. A. Characteristics of the protective response of BALB/c mice immunized with a purified Plasmodium yoelii schizont antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):609–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R., Hyde J. E., Goman M., Simmons D. L., Hope I. A., Mackay M., Scaife J., Merkli B., Richle R., Stocker J. Major surface antigen gene of a human malaria parasite cloned and expressed in bacteria. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):379–382. doi: 10.1038/311379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera M. A., Rosero F., Herrera S., Caspers P., Rotmann D., Sinigaglia F., Certa U. Protection against malaria in Aotus monkeys immunized with a recombinant blood-stage antigen fused to a universal T-cell epitope: correlation of serum gamma interferon levels with protection. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):154–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.154-158.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera S., Herrera M. A., Perlaza B. L., Burki Y., Caspers P., Döbeli H., Rotmann D., Certa U. Immunization of Aotus monkeys with Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage recombinant proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. Immunization against blood-stage rodent malaria using purified parasite antigens. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):361–364. doi: 10.1038/294361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R., Nicholls S. C. Immunization against Plasmodium falciparum with recombinant polypeptides produced in Escherichia coli. Parasite Immunol. 1988 Nov;10(6):607–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A. The precursor to major merozoite surface antigens: structure and role in immunity. Prog Allergy. 1988;41:72–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui G. S., Hashimoto A., Chang S. P. Roles of conserved and allelic regions of the major merozoite surface protein (gp195) in immunity against Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1422–1433. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1422-1433.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. P. Cloning and analysis of the gene encoding the 230-kilodalton merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium yoelii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Oct;36(3):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majarian W. R., Daly T. M., Burns J. M., Jr, Long C. A. Plasmodium yoelii: characterization of a protective idiotype during malarial infection in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Dec;67(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majarian W. R., Daly T. M., Weidanz W. P., Long C. A. Passive immunization against murine malaria with an IgG3 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3131–3137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride J. S., Newbold C. I., Anand R. Polymorphism of a high molecular weight schizont antigen of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):160–180. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy V. F., Rowan W. C., Page M. J., Holder A. A. Expression of hybrid malaria antigens in insect cells and their engineering for correct folding and secretion. Parasitology. 1990 Apr;100(Pt 2):177–183. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000061175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. E., Rocco L. J. Sialic acid-dependent binding of Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen, Pf200, to human erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3190–3196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Loche M., Dedet J. P., Roussilhon C., Fandeur T. Immunization against Plasmodium falciparum asexual blood stages using soluble antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):67–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirson P. J., Perkins M. E. Characterization with monoclonal antibodies of a surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui W. A., Tam L. Q., Kramer K. J., Hui G. S., Case S. E., Yamaga K. M., Chang S. P., Chan E. B., Kan S. C. Merozoite surface coat precursor protein completely protects Aotus monkeys against Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Mackay M., Goman M., Scaife J. G. Allelic dimorphism in a surface antigen gene of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]