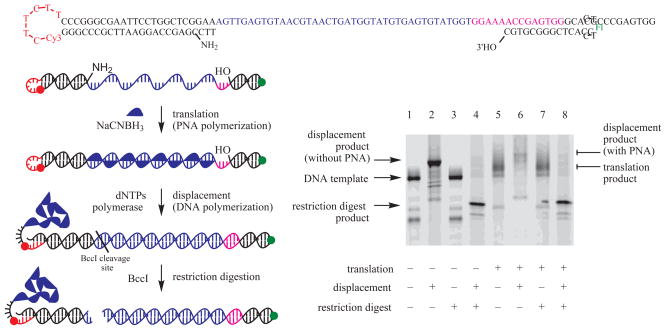
Figure 4. Translation of a DNA template into PNA and displacement of the resulting PNA strand.
Following PNA polymerization (lane 5) under conditions described in Figure 2, the PNA strand is displaced by primer extension of the 3′ hairpin using Herculase DNA polymerase II and dNTPs (lane 6). DNA polymerization to the end of the template strand (through the 5′ stem-loop) generates an 84-base pair DNA duplex that can form as a mutually exclusive alternative to the 40-base pair PNA-DNA heteroduplex and 24-base pair DNA-DNA stem. Successful strand displacement creates a double-stranded BccI restriction endonuclease cleavage site. The BccI-mediated cleavage of the primer extension product (lanes 4 and 8) is therefore consistent with displacement of the PNA strand. The red dot represents a Cy3 backbone spacer that blocks subsequentual DNA polymerization. The green dot represents a fluorescein group. The denaturing PAGE gel shown is visualized by imaging fluorescein fluorescence. Reactions shown in lanes labeled “translation–” lacked NaCNBH3; those in lanes labeled “displacement–” lacked DNA polymerase; those in lanes labeled “restriction digestion–” lacked BccI.