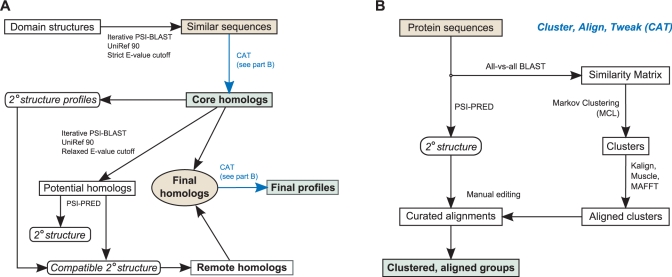
Figure 1.
Semi-automatic algorithm for defining high-quality domain models. (A) Bona fide domain members which have had their structure solved are subjected to iterative PSI-BLAST searches (30) against the UniRef90 (31) database with a stringent E-value threshold. The resulting sequences are then clustered, aligned and edited (CAT, part B) to form the set of core homologs. Remote homologs are identified by the same procedure with a much relaxed threshold and then removing hits that do not match a secondary structure type associated with at least one core homolog. The resulting remote homologs are combined with the core homologs and then subjected to the CAT process to produce the final domain model(s). (B) The CAT sub-algorithm is a divide-and-conquer method for addressing the extreme sequence divergence present in signal transduction families. Markov Clustering Linkage (32) simulates a random-walk through all-versus-all BLAST results and produces clusters of related members. After aligning and editing each individual subgroup, they are further combined into one or more final curated alignments.