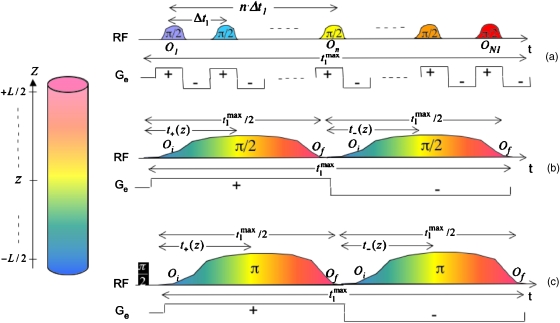
Figure 2.
Description of the combined gradient∕rf manipulations underlying the indirect-domain spatial encoding strategies considered in this work. (a) Discrete real-time scheme involving a train of π∕2 pulses applied in synchrony with an oscillating ±Ge waveform. (b) Continuous real-time scheme whereby chirped excitation and storage π∕2 pulses are applied in the presence of a single bipolar ±Ge oscillation. (c) Idem but based on a phase-modulated, constant-time spin evolution imparted by a pair of chirped π pulses. Spatiotemporal encoding efficiencies for the different sequences are C=N1Δt1∕L, , and , respectively; the timings n Δt1, t+(z), and t−(z) refer to the fate of the lightest (yellow) z coordinate.