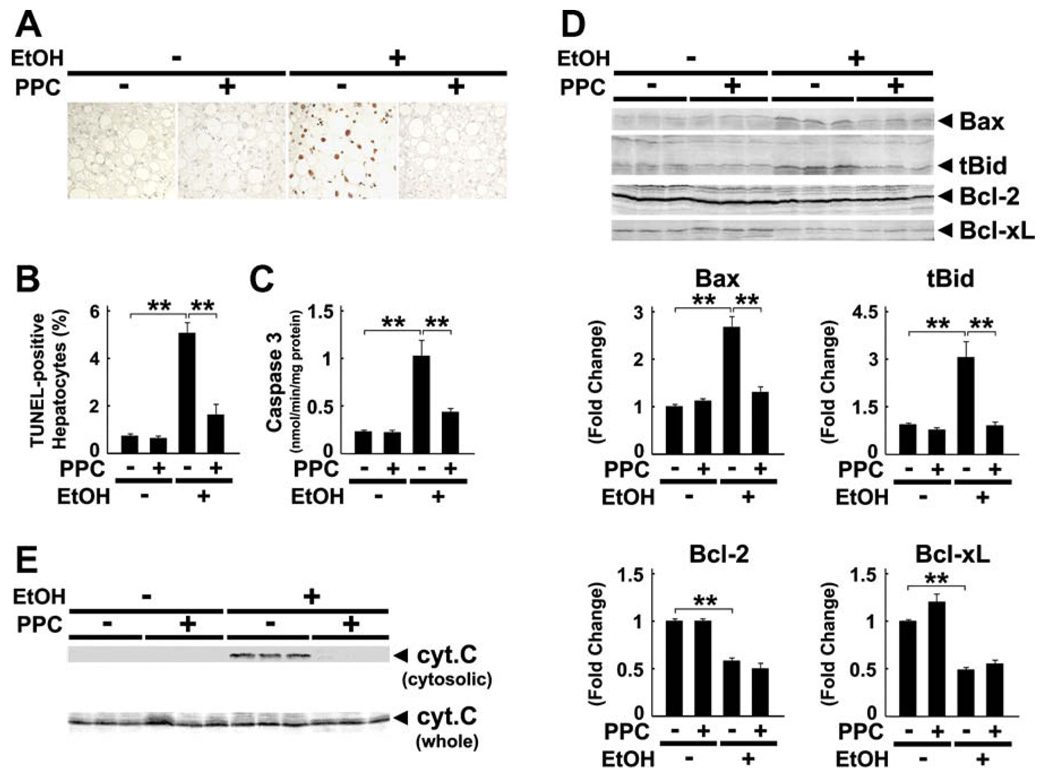
Fig. 8.
Ethanol-induced hepatocyte apoptosis was prevented by PPC treatment in Ppara−/− mice. (A and B) Apoptotic hepatocytes as determined by TUNEL staining. Two-hundred hepatocytes were examined for each section, and the number of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes was expressed as a percentage. Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6/group). **P < 0.01. (C) Activity of caspase 3. **P < 0.01. (D) Immunoblot analysis of apoptosis-related proteins. The same samples in Fig. 3D (whole liver lysate, 50 µg of protein) were used. The bands shown are representative of four independent experiments. Band intensity was quantified densitometrically, normalized to that of actin, and subsequently normalized to that in control Ppara−/− mice. Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6/group). tBid, truncated Bid; **P < 0.01. (E) Immunoblot analysis of cytochrome c (cyt. c). The same samples used in Fig. 3D (whole liver lysate, 50 µg of protein) and Fig. 6B (cytosolic fraction, 100 µg of protein) were adopted. Results are representative of four independent experiments.