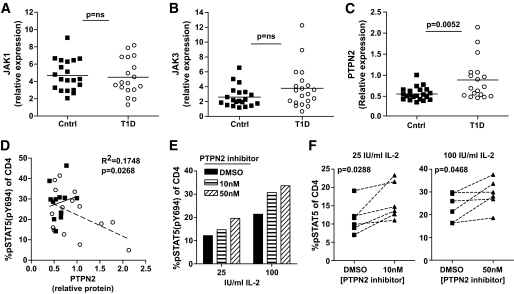
FIG. 6.
Altered expression of molecules in the IL-2R signaling cascade in CD4+ T-cells of type 1 diabetic subjects. CD4+ T-cells were isolated from fresh PBMCs of control and type 1 diabetic subjects, and whole-cell protein lysates were analyzed by Western blot. Immunoblots were probed with JAK1-, JAK3-, and PTPN2-specific antibodies and an anti-TFIIB antibody as a loading control. Protein expression was determined by densitometry, normalizing each sample to TFIIB and expressing total protein levels relative to a Jurkat control present on each blot. Total JAK1 (A) and JAK3 (B) protein expression was compared between control (n = 20) and type 1 diabetic (n = 18 and 20 for JAK1 and JAK3, respectively) subjects. C: PTPN2 protein expression was compared between control (n = 21) and type 1 diabetic (n = 18) subjects. Significance was determined using an independent Student t test. D: Thawed PBMCs from these same samples were assayed for pSTAT5 upon exposure with 100 IU/ml IL-2 for 10 min as in Fig. 4. Using linear regression, protein expression was compared with pSTAT5 for control (n = 13) and type 1 diabetic (n = 15) subjects. Correlation between PTPN2 protein expression in the total population (control and type 1 diabetic subjects combined) and pSTAT5 is noted in the graph. Solid trend line (R2 = 0.02, P = 0.6) and squares denote control subjects, and dashed trend line (R2 = 0.234, P = 0.067) and open circles denote type 1 diabetic subjects. E: Thawed PBMCs from the type 1 diabetic subject with the highest PTPN2 expression or (F) type 1 diabetic subject with PTPN2 expression above the mean 0.8 (n = 6) were incubated with a PTPN2 inhibitor (compound 8 in [29]) for 30 min prior to stimulation with IL-2 for 10 min as in Fig. 4.