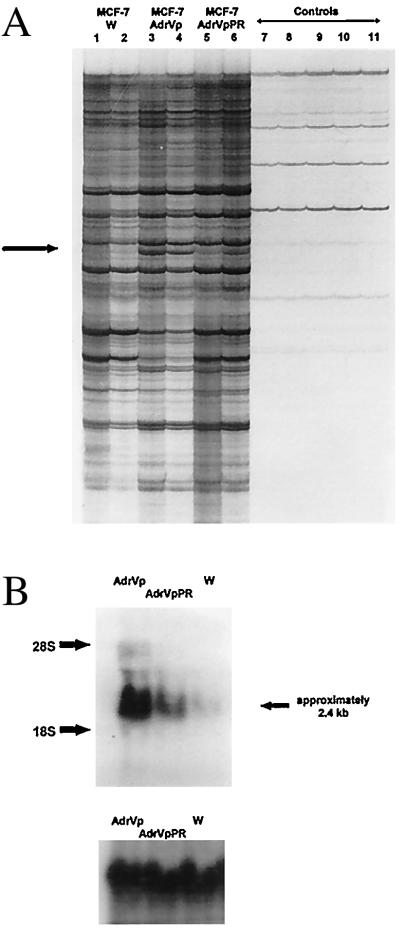
Figure 1.
(A) RNA fingerprinting of MCF-7 cells. Total cellular RNA was treated with DNase, reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and amplified by PCR using upstream and downstream primers and radiolabeled [33P]dATP. The figure depicts a portion of the autoradiograph of a 5% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the PCR mixture by using the primer pair P6 and T9. Lanes 1, 3, and 5 are reaction mixtures in which cDNA diluted 1:10 was added; lanes 2, 4, and 6 represent reaction mixtures in which cDNA diluted 1:40 was added. Lanes 7 and 8 are H2O controls, in which sterile water was added to the PCR mixture in place of cDNA. Lanes 9, 10, and 11 are RNA controls, in which 0.02 μg of cellular RNA from MCF-7/W, MCF-7/AdrVp, or MCF-7/AdrVpPR cells was added instead of cDNA. These RNA controls served to indicate contamination of the RNA with genomic DNA. The arrow indicates a PCR product representing an mRNA species overexpressed in MCF-7/AdrVp cells, compared with MCF-7/W or MCF-7/AdrVpPR cells. This product was excised from the gel for further amplification by PCR. (B) Northern blot hybridization (Upper) of mRNA from MCF-7/W, MCF-7/AdrVp, or MCF-7/AdrVpPR cells by using the 795-bp PCR product obtained from RNA fingerprinting studies and isolated by TA cloning as a probe after labeling with [32P]dCTP (Prime-a-Gene labeling kit, Promega). To control for equivalence in sample loading, the blot was stripped and rehybridized with a radiolabeled probe for 18S RNA (Lower).