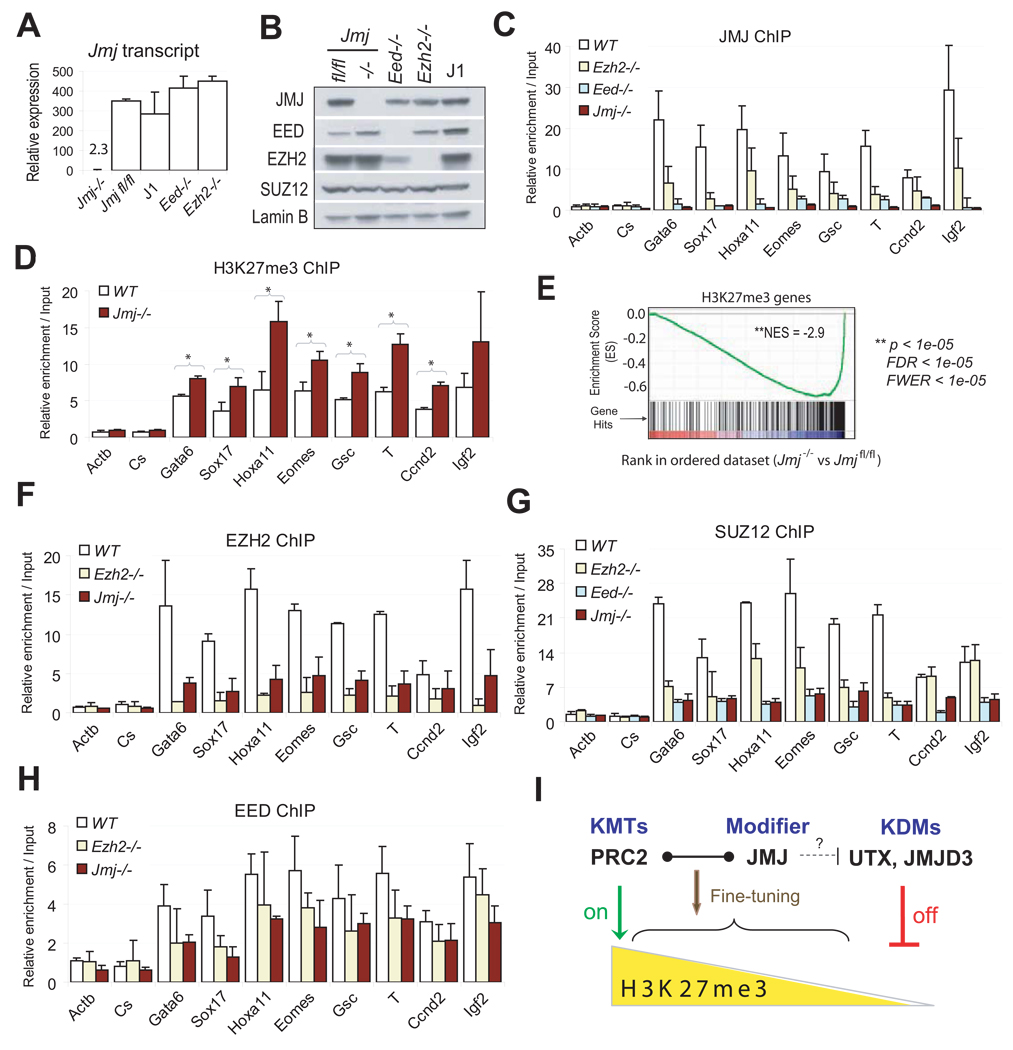
Figure 5. Characterization of Jmj−/− ESCs.
(A) Reverse transcription (RT) and qPCR analysis of Jmj transcripts in wild-type and mutant ESCs. Error bars are standard deviations of relative expression to GADPH.
(B) Western blotting analysis of wild-type and mutant ESCs.
(C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of JMJ in wild-type (WT) and mutant ESCs.
(D) ChIP-qPCR analysis of the H3K27me3 mark in Jmj−/− and wild-type ESCs. * indicates p < 0.05 by a Student's paired t-Test with a two-tailed distribution.
(E) GSEA profile of the set of H3K27me3 target genes. Genes are ranked into an ordered list based on the correlation between their expression levels in Jmj−/− and Jmjfl/fl ESCs. Genes which are upregulated in Jmj−/− ESCs are ranked at the top of the list (left, red), while downregulated genes are ranked toward the bottom (right, blue). The middle portion of the plot shows where the members of the gene set (indicated by vertical lines) locate in the ranked list shown in the bottom portion. The green curve in the top portion shows the running enrichment score (ES) for the gene set as the analysis walks down the ranked list. The distribution of H3K27me3 target genes appear toward the bottom of the rank list with a normalized enrichment score (NES) of −2.9. Statistic significance is indicated by nominal p value, familywise-error rate (FWER) and false discovery rate (FDR).
(F) – (H) ChIP-qPCR analysis of EZH2 (F), SUZ12 (G) and EED (H) at PRC2 targets in wild-type and mutant ESCs. In (C), (D) and (F)–(H), error bars are standard deviations of relative enrichments based on at least three biological repeats. The Actb promoter and an intergenic region (Cs) serve as negative controls.
(I) A model shows dynamic regulation of H3K27me3. PRC2, the H3K27 methyltransferase complex (KMT), and UTX and JMJD3, the H3K27me3 demethylases (KDM), represent on-off controls on H3K27me3. While PRC2 catalyzes the formation of H3K27me3, UTX and JMJD3 demethylate H3K27me3. In contrast to KMTs and KDMs, JMJ, as a modifier of PRC2, fine-tunes the levels of H3K27me3 by regulating the activity and recruitment of PRC2.