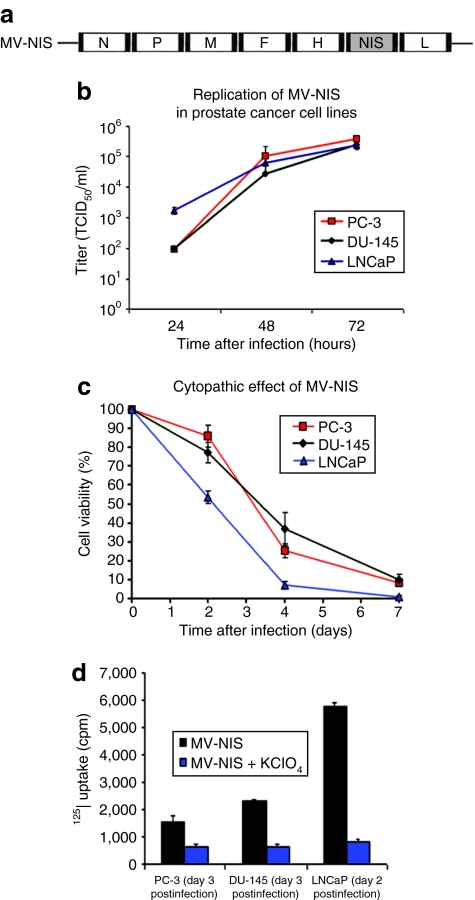
Figure 1.
Replication and cytopathic effect of MV-NIS on prostate cancer cell lines and in vitro Iodide-125 (125I) uptake of cells infected with MV-NIS. (a) Schematic representation of measles virus–sodium iodide symporter (MV-NIS). The complementary DNA encoding for the human thyroidal NIS was inserted downstream of the hemagglutinin (H) gene (N, nucleoprotein gene; P, phosphoprotein gene; M, matrix protein gene; F, fusion protein gene; L, large protein gene). (b) MV-NIS efficiently replicates in PC-3, DU-145, and LNCaP prostate cancer cells as demonstrated by one-step growth curves for cell-associated virus. (c) Cytopathic effect of MV-NIS on PC-3, DU-145, and LNCaP cells at multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1.0. Cell viability was determined by the cell proliferation kit I (MTT) colorimetric assay. Monolayer cell cultures were completely eradicated by day 7. (d) In vitro Iodide-125 (125I) uptake of prostate cancer cells infected with MV-NIS with or without potassium perchlorate (KClO4). Prostate cancer cell lines were infected with MV-NIS at a MOI of 1.0. Infected cells cocultured with KClO4, a competitive inhibitor of iodide uptake by NIS, were used as controls. Significantly more radioiodide uptake was observed in MV-NIS-infected cells as compared to controls in all prostate cancer cell lines tested (P < 0.05 for all comparisons). Results are presented as the means of three independent experiments ± SEM.