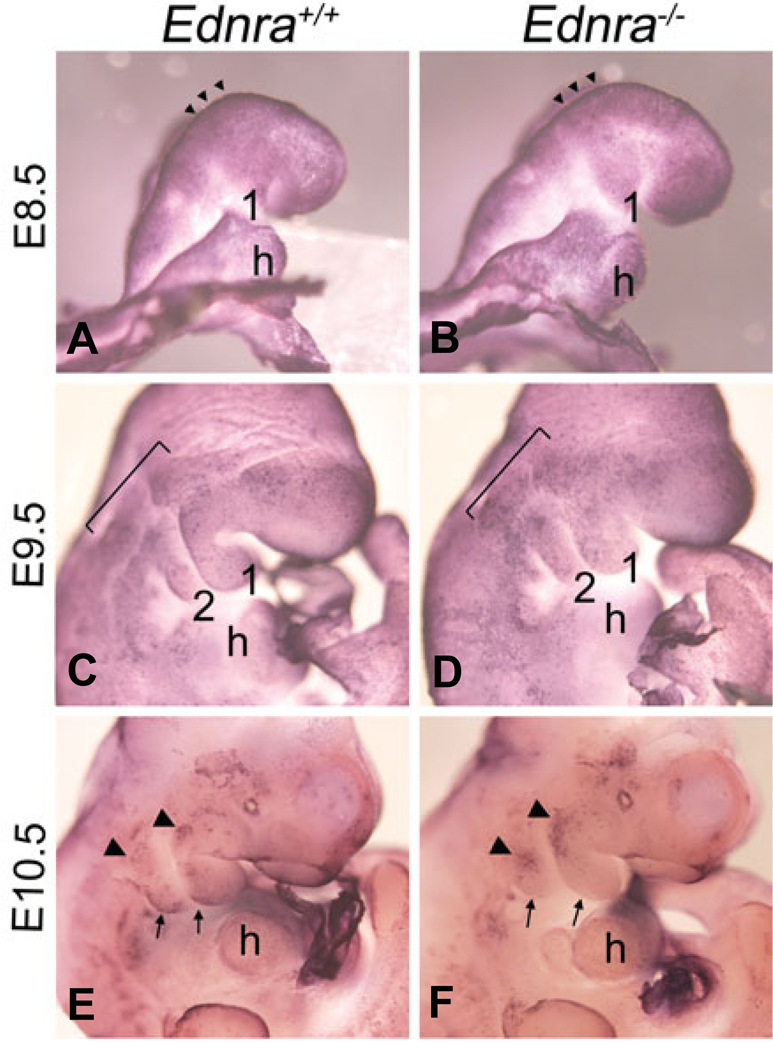
Fig. 5. Whole mount apoptosis analysis in Ednra−/− embryos.
Lateral and ventral views of wild type (A,C,E) and Ednra−/− (B,D,F) embryos at E8.5 (A,B), E9.5 (C,D) and E10.5 (E,F) following whole mount TUNEL analysis, with NBT/BCIP as the substrate, which produces a blue deposit. (A,B) At E8.5, apoptosis is confined to the neural fold in the midbrain and hindbrain regions (arrowheads) of both wild type (A) and Ednra−/− (B) embryos. (C,D) In E9.5 wild type embryos, scattered apoptosis is observed proximal to and within pharyngeal arches one and two (C). In E9.5 Ednra−/− embryos, apoptosis is observed in a similar pattern to that of wild type embryos, though the qualitative level of apoptosis appears higher, especially in the arches (D). (E,F) In the pharyngeal arch region of E10.5 wild type embryos, apoptosis is observed in cells at the proximal aspect of arches one and two (arrowheads) and in cells along the caudal aspects of both arches (arrows) (E). In E10.5 Ednra−/− embryos, apoptosis is more prominent in the proximal aspects of the mandibular and second arches (arrowheads) but is not apparent in the caudal aspects of arches one and two (arrows) (F). h, heart.