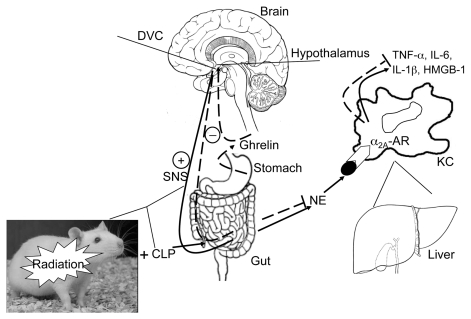
Figure 1.
Whole body radiation (Radiation) combined with polymicrobial sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) (RCI) activates the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and causes the release of norepinephrine (NE) from the sympathetic fibers in the gut. The NE then travels through the portal vein into the liver. While in the liver, NE binds to the α2A-adrenoceptors (α2A-AR) and activates the signaling pathway(s) responsible for the production and release of proinflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and HMGB-1, from Kupffer cells (KC). Ghrelin, a stomach-derived peptide, reaches the dorsal vagal complex (DVC) in the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier, stimulates GHSR-1a receptors (ghrelin receptors), activates the vagus nerve and in turn, through the cholinergic pathways, downregulates TNF-α and other proinflammatory cytokines. While activating the cholinergic pathway, ghrelin can inhibit the SNS, decrease the release of the sympathetic neurotransmitter NE, and cause the downregulation of the proinflammatory cytokines as well. Therefore, ghrelin’s beneficial effect in RCI is caused by the rebalance of the dysregulated sympathetic/parasympathetic nervous systems. HMGB-1, high-mobility-group B1.