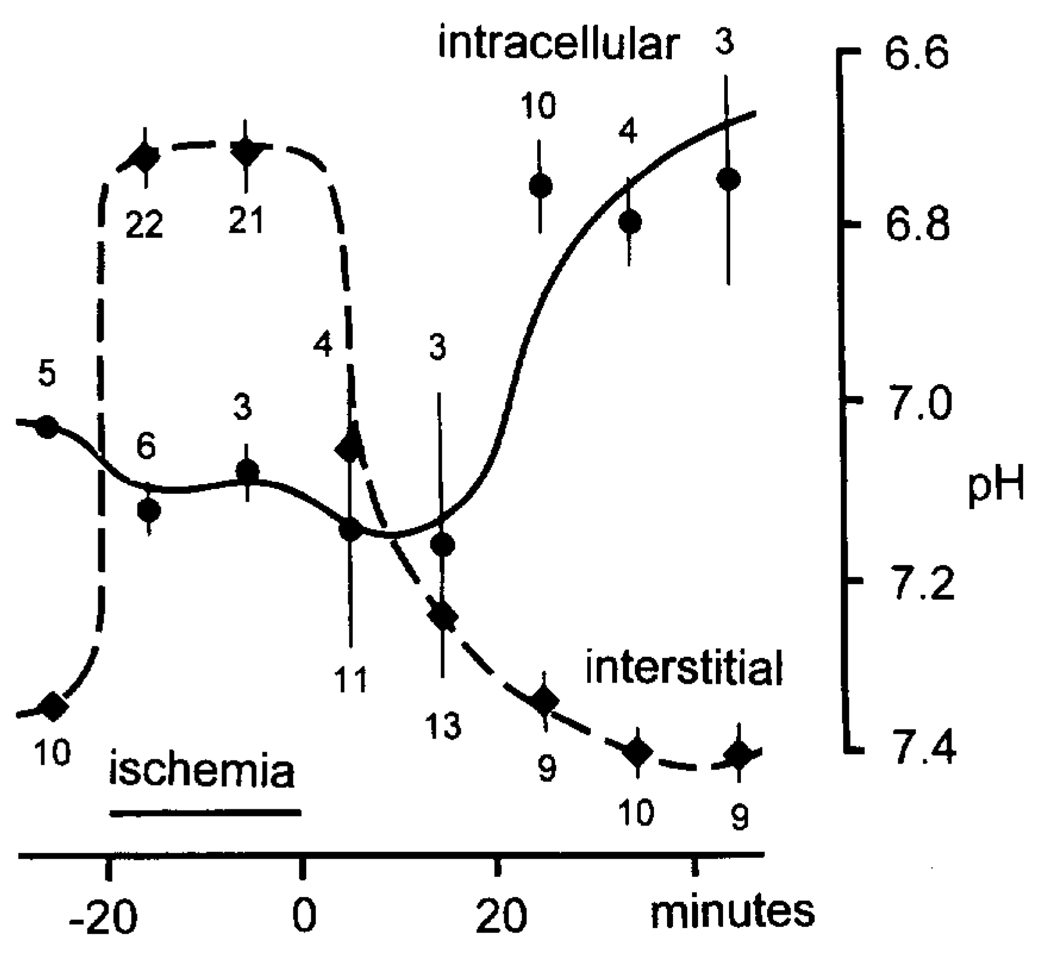
FIG. 2.
Astroglial alkalosis during normoglycemic, nearly complete ischemia. pH-ISMs were used to measure pHi in presumed glia prior to, during, and several minutes after global ischemia. Before and after ischemic depolarization, cells were identified as astrocytes by their high membrane potential, low membrane impedance, and absence of synaptic or injury discharges. A microelectrode taper that selectively penetrates astrocytes under normal conditions was chosen for recordings during anoxic depolarization. Horseradish peroxidase injections using this taper have consistently stained astrocytes (24). Triangles refer to interstitial recordings; dots indicate intracellular recordings. Recordings were grouped into 10-min intervals and averaged. The vertical bars through points represent standard error of means. Interstitial numbers below triangles, and intracellular numbers above dots, represent the number of recordings for a particular 10-min interval. Note that, during ischemia, astrocytes were alkaline as the interstitium acidified. The measurements also suggest that astrocytes may become slightly more alkaline relative to their own normal baseline pH.