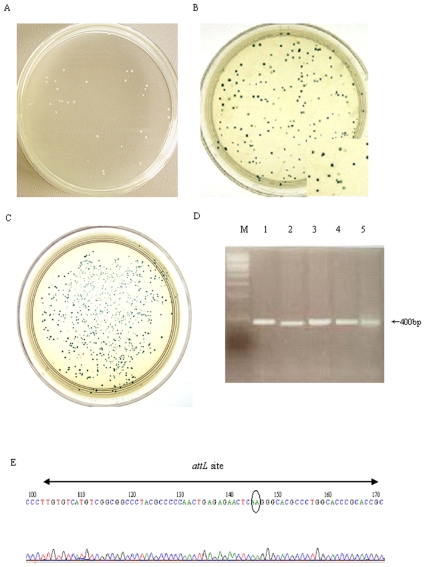
Figure 2. Recombination assay of phiC31 mutants in E. coli.
Each mutant plasmid and its report plasmid were co-transformed into Top10 bacteria, respectively. The bacteria were then plated to form colonies on double antibiotic selecting agar plates containing X-Gal. When mutant recombinases still have their recombination ability, this recombination event consequently produces white colonies (A). When mutant integrase have lost or reduced recombination ability, It is observed that mixture of white and blue colonies (B) or only blue coloneies (C) on the plates. To further verify site-specific recombination at molecular level, the white colonies were picked, and plasmid DNA was subjected to PCR with specific primers that would amplify a 400-bp product only from the recombinant. DNA from 5 white colonies was subjected to PCR with specific primers, and a 400-bp product got amplified (D). The sequence of this PCR product contained the predicted chimeric attL site, comprising an attP arm (left) and attB arm (right) around the core AA dinucleotides (gray ellipse).