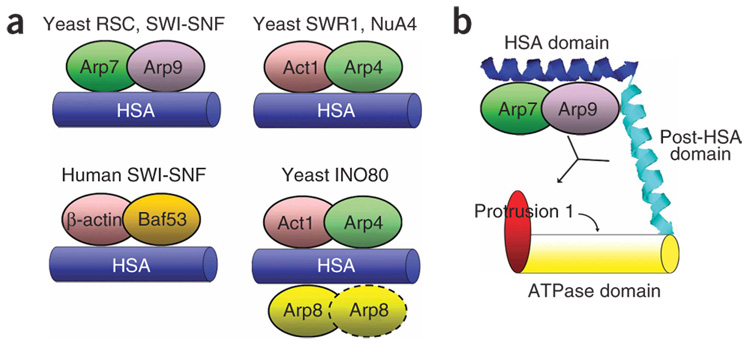
Figure 7.
Summary of HSA domain complexes and a model for HSA–ARP regulation of ATPase activity via the adjacent post-HSA domain and protrusion 1. (a) The HSA domains from yeast modifying complexes RSC (Sth1), SWI-SNF (Snf2), SWR1 (Swr1), NuA4 (Eaf1), INO80 (Ino80) and human SWI-SNF (BRG1) nucleate binding of their respective ARP–ARP or ARP–actin members. (b) The HSA–ARPs, post-HSA and protrusion 1 domains interact to regulate the function of the ATPase. Actin-related proteins bind strongly to the HSA, with a weak interaction with the post-HSA also detected. The ARPs and protrusion 1 positively regulate ATPase activity, and the ability of the ARPs to influence (or bind) protrusion 1 may be regulated by the post-HSA domain.