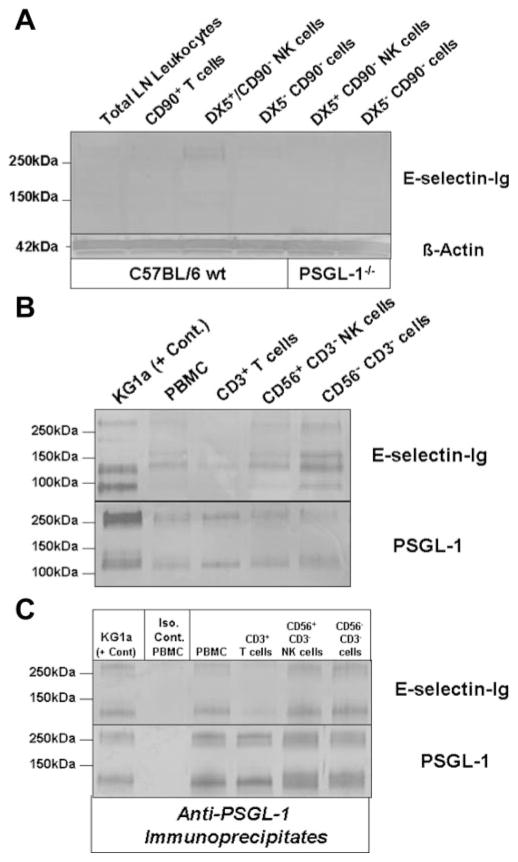
FIGURE 4.
E-selectin-binding PSGL-1 is expressed on NK cells. A, Western blot analysis of E-selectin ligand expression was performed on DX5+ CD90− NK cell lysates (40 μg/lane) from both wt and PSGL-1−/− mice. Compared with total LN leukocyte, CD90+ T cell or DX5− CD90− cell lysates, a demonstrable E-selectin-Ig-stained band was evident in DX5+ CD90− NK cell lysate at 260 kDa, which was absent in DX5+ CD90− NK cell lysate from PSGL-1−/− mice. Protein loading was controlled for by staining lysates with anti-β-actin. B, Western blot analysis of E-selectin ligand expression was performed on control KG1a cell lysate and on total PBMC, CD3+ T cell, CD56+ CD3− NK cell, and CD56− CD3− cell lysates (30 μg/lane). Compared with E-selectin-Ig-stained bands principally represented by CD44 (95kDa) and PSGL-1 (130 and 260kDa) in KG1a lysate, there were also E-selectin-Ig-stained bands at 130 and 260 kDa in CD56+ CD3− NK cell lysates that comigrated with KG1a PSGL-1, in addition to another band at 155 kDa. Protein loading was controlled by staining lysates with anti-PSGL-1 moAb KPL-1. C, To confirm the E-selectin-binding function of PSGL-1, PSGL-1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-PSGL-1 moAb KPL-1 or isotype Ab from component cell lysates and Western blotted with E-selectin-Ig or KPL-1. As shown, PSGL-1 bound E-selectin-Ig in all immunoprecipitates (C). Experiments were performed a minimum of three times.