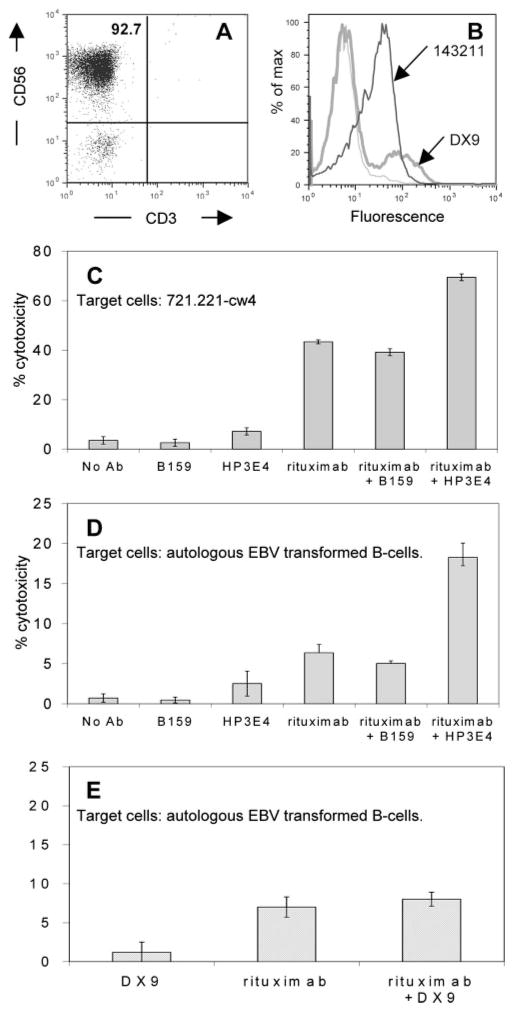
FIGURE 6.
ADCC promotion by blocking inhibitory self-recognition receptor on fresh purified NK cells. NK cells were purified from a whole blood sample obtained from a healthy donor as described in Materials and Methods. A, Purity of NK cells was analyzed by flow cytometry staining with CD3-FITC and CD56-PE Abs. B, Flow cytometric analysis was used to determine KIR expression on purified NK cells. Staining with 143211 Ab (thick black histogram) binding KIR2DL1 and DX9 Ab (thick gray histogram) binding KIR3DL1) is shown. Thin gray histogram is secondary Ab alone. NK cells from this donor (expressing KIR2DL1 on all NK cells, but KIR3DL1 on only a subpopulation, see Fig. 5B) were incubated with 51Cr-labeled 721.221-Cw4 cells (C) or with autologous EBV-transformed B cells (D and E) at a 10:1 E:T ratio. Cytotoxicity was calculated using a 4-h 51Cr release assay in the presence of B159 binding CD56 (C and D), HP3E4 binding KIR2DL1, KIR2DS1, and KIR2DS4 (C and D), DX9 binding KIR3DL1 (E), and rituximab (C–E) in different combinations as indicated. All Abs were used at 1 μg/ml concentration. Results shown are mean ± SD of one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments.