Fig. 5.
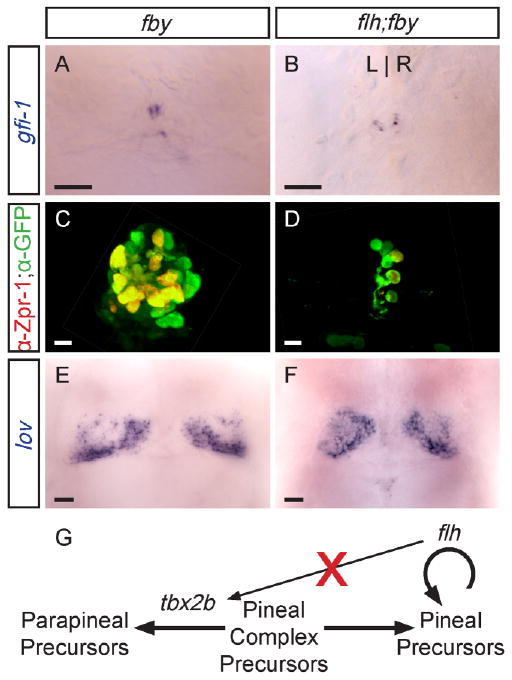
Double homozygous flh;fby mutants exhibit an additive phenotype. All panels are dorsal views of the epithalamus of 4 d larvae. A: In fby single mutants or (B) flh;fby double mutants, only a few disorganized parapineal cells are specified, and they fail to migrate to the left side of the brain. C: fby single mutants form a pineal organ. D: flh;fby double mutant larvae have both a reduced pineal, similar to flh single mutants (compare to Fig. 3D). E: In fby single mutants and (F) flh;fby double mutants, reduced lov expression is detected in the left habenula. Scale bars = 25 μm. G: Summary of tbx2b and flh activity in pineal complex development. The activity of tbx2b gives parapineal precursors their identity, while flh is needed for proliferation of pineal precursor cells. Expression of tbx2b does not require flh activity.
