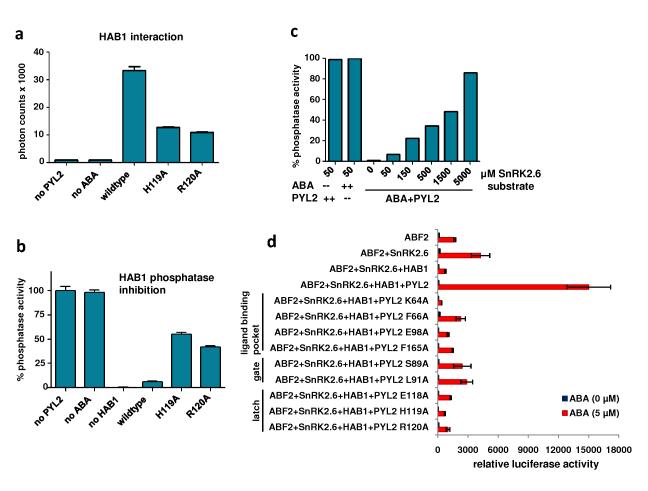
Fig. 5. Mutational analysis of PYL2 and HAB1 interface residues.
a+b, Functional analysis of mutations in PYL2 latch residues by (A) HAB1 interaction as determined by AlphaScreen (n=3, error bars=SD) and by (B) HAB1 phosphatase activity (n=3, error bars=SD). c, Increasing concentrations of the SnRK2.6 substrate overcomes HAB1 inhibition by ABA-bound PYL2. Uninhibited HAB1 phosphatase activity (absence of either ABA or PYL2) is shown as control. d, Reconstituted ABA signaling pathway for gene expression in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. PYL2, HAB1, SnRK2.6 and ABF2 expression vectors were cotransfected into protoplasts together with a luciferase reporter plasmid driven from the promoter of the ABA-responsive RD29B gene. Mutations in the PYL2 ligand binding pocket (K64A, F66A, E98A, F165A), the SGLPA gate (S89A and L91S), and the latch (E118A, H119A, R120A) are defective in the reconstituted signaling pathway (n=3, error bars=SEM).