Fig. 2.
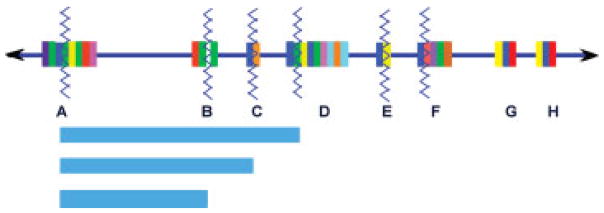
A schematic depiction of low copy repeats (LCRs) that mediate genomic instability on chromosome 22. The 22q11 region is enlarged, represented by the blue line with arrows at both ends, and is drawn from centromere (left) to telomere (right). The complex modular LCRs that characterize this region are represented by the multicolored vertical rectangular boxes, each color representing a stretch of DNA sequence repeated in multiple LCRs. The BCRL module is depicted by a royal blue box that is present in all of the LCRs except LCR-B. Zigzag lines represent the locations of multiple recurrent breakpoints including those for the deletions seen in the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome patients, the duplications seen in the Cat Eye syndrome, and the translocations involving 22q. Light blue horizontal rectangles on the lower portion of the diagram indicate the extent of the prevalent, recurrent LCR-mediated 22q deletions seen in the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. It has been demonstrated that palindromic AT rich repeats in the white “gap” indicated in LCR-B of 22q11 can form hairpins and cruciforms that mediate translocations between chromosome 22 and several other partner chromosomes. Concept and design courtesy of Tamim H. Shaikh, Ph.D.