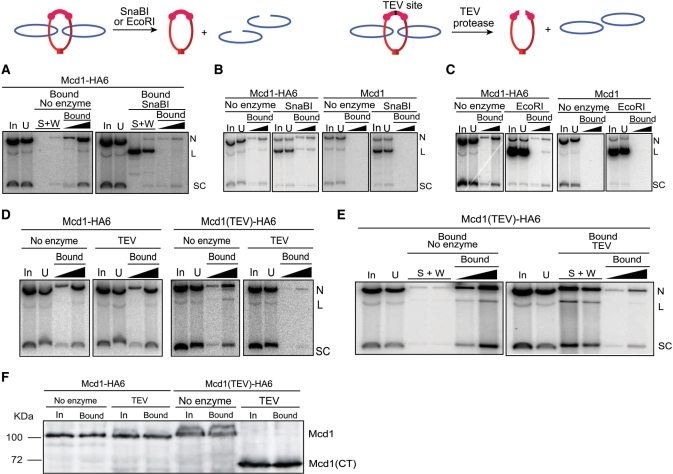
Figure 2.
Release of an STB reporter plasmid from cohesin’s grasp by linearizing DNA or cleaving Mcd1. The consequences of cutting DNA or protein on the topological association between plasmid and cohesin are schematically indicated. (A) Cohesin associated pSG4 was adsorbed on HA-antibody and immobilized on Protein A beads as described under Figure 1. After digestion with SnaBI, DNA released into the supernatant (S) and wash fractions (W) and that retained on the beads (Bound) were analyzed. (B and C) SnaBI or EcoRI digestion was performed in the cleared lysates prior to immunoprecipitation by HA-antibody. (D) Cleared lysates were treated with TEV protease, and then subjected to pull-down by HA-antibody and Protein A beads. (E) Cohesin bound plasmid from cleared lysates was treated with HA-antibody, trapped on Protein A beads, and subjected to TEV protease treatment. (F) Cleavage of Mcd1-HA6 by TEV protease in the cleared lysates (corresponding to the DNA analysis shown in D) was monitored by western blotting using HA-antibody. The amount of protein analyzed from the bead-bound fraction was four equivalents of that from the input. The identity of the weak band above Mcd1 seen in some of the lanes is not known. Its mobility would be consistent with phosphorylation of Mcd1, which occurs during the establishment of cohesion in response to DNA damage (27).