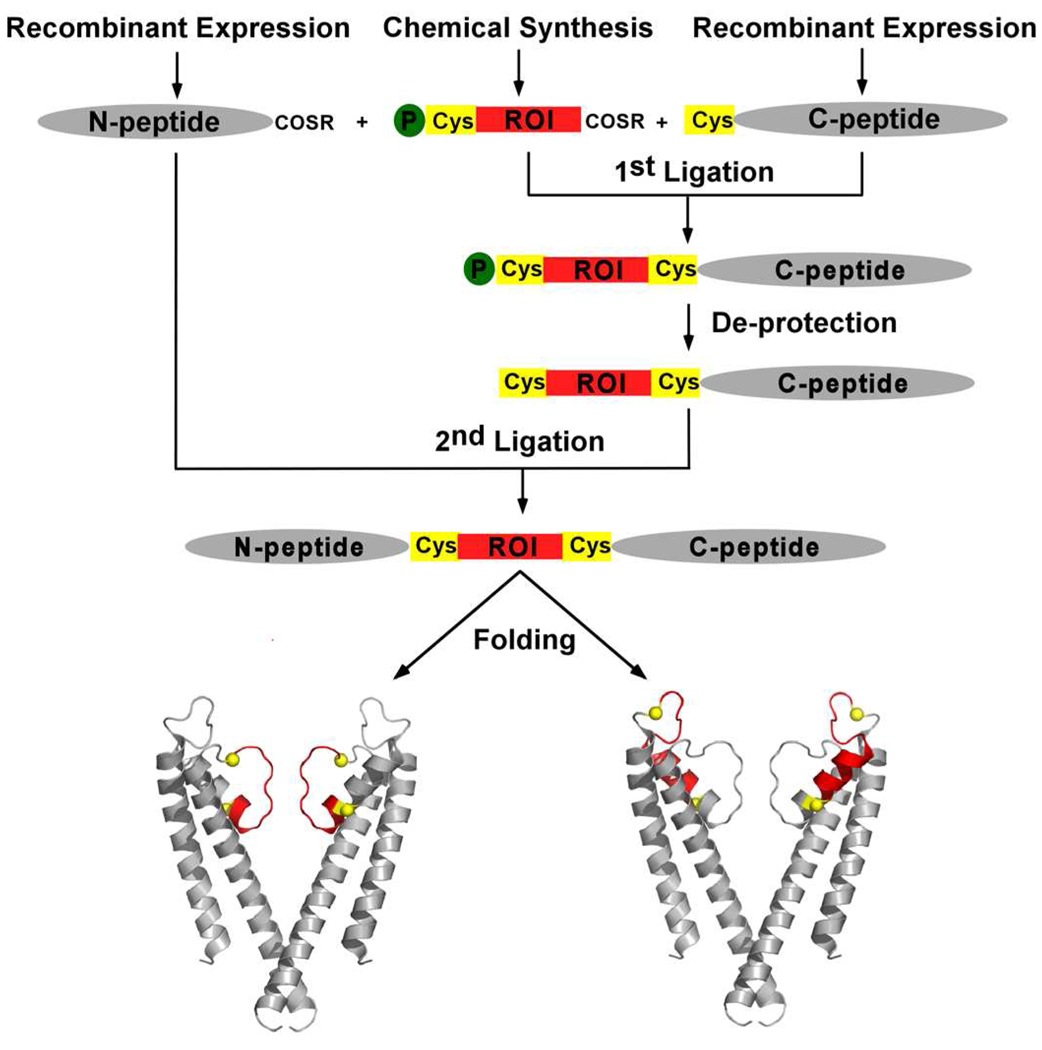
Fig. 1. The modular semi-synthesis of the KcsA channel.
The KcsA polypeptide is synthesized by two sequential ligation reactions. The first ligation reaction between a recombinantly expressed C-peptide and a chemically synthesized region of interest (ROI) peptide yields the intermediate peptide. The Thz protecting group (green sphere) on the N-terminal Cys of the intermediate peptide is removed and the de-protected intermediate peptide is ligated to a recombinantly expressed N-peptide thioester to yield the KcsA polypeptide. The KcsA polypeptide is folded in vitro to the native state. The modular strategy can be used to assemble semi-synthetic KcsA channels in which the selectivity filter (left) or the pore helix (right) is obtained by chemical synthesis. The protein segments obtained by chemical synthesis are colored red while the protein segments obtained by recombinant means are colored grey. The ligation sites are represented by yellow spheres.