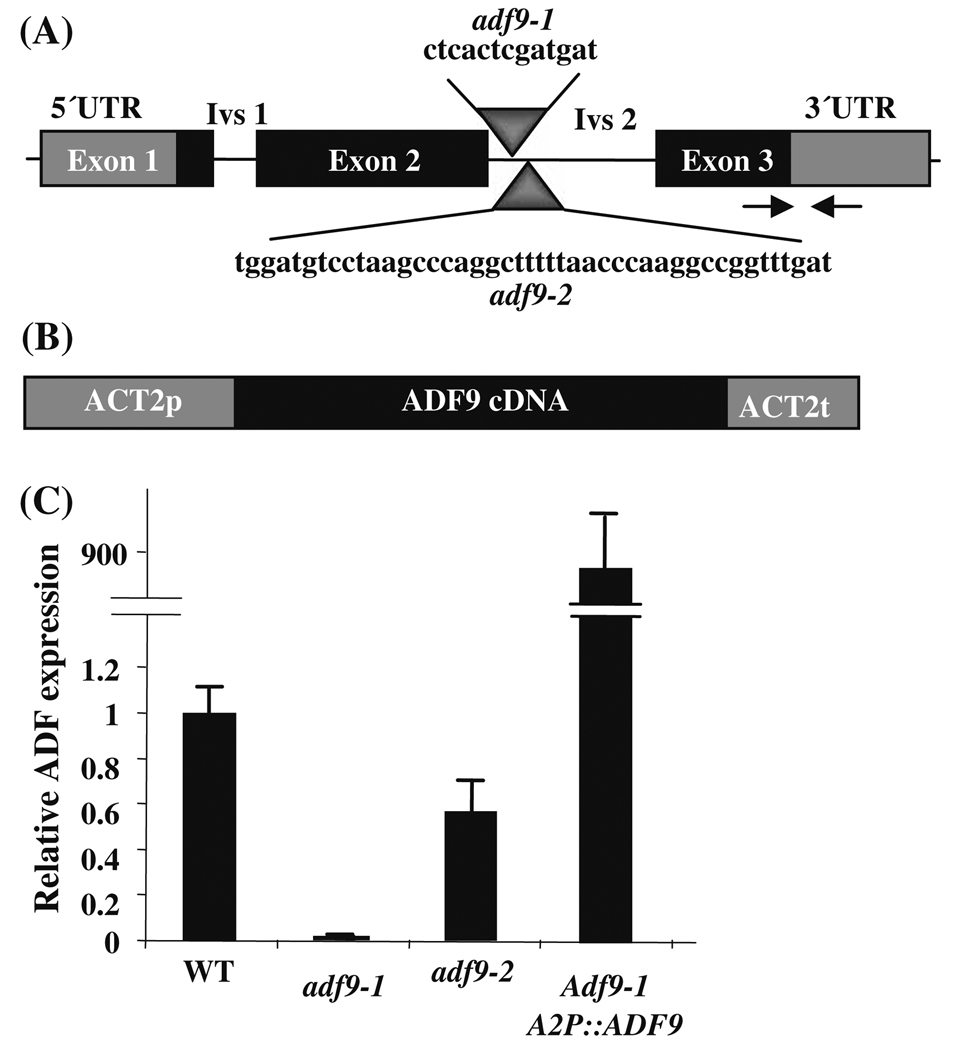
Fig. 1. Gene constructs and reduced mRNA expression in adf9-1 and adf9-2 mutants.
(a) The T-DNA insertions in adf9-1 and adf9-2 were both located within intron 2, were separated at their 5′ ends by 37 bp, and were not overlapping. The intron sequences deleted from each intron and replaced by T-DNA are shown for each insertion. Arrows indicate the location of the qRT-PCR primers used to assay ADF9 transcript levels. (b) The cDNA encoding region of ADF9 was cloned within the actin ACT2 constitutive expression cassette A2pt. A2pt::ADF9 was used to complement adf9-1. (c) The adf9-1 and adf9-2 mutations produced a 95% and 50% drop in levels of transcript relative to wild-type, respectively. The adf9-1 insertion may disrupt an important transcriptional enhancer or splicing sequence resulting in lower steady state mRNA levels. Complementing adf9-1 with A2pt::ADF9 resulted in an approximately 900-fold increase in ADF9 transcript levels over wild-type