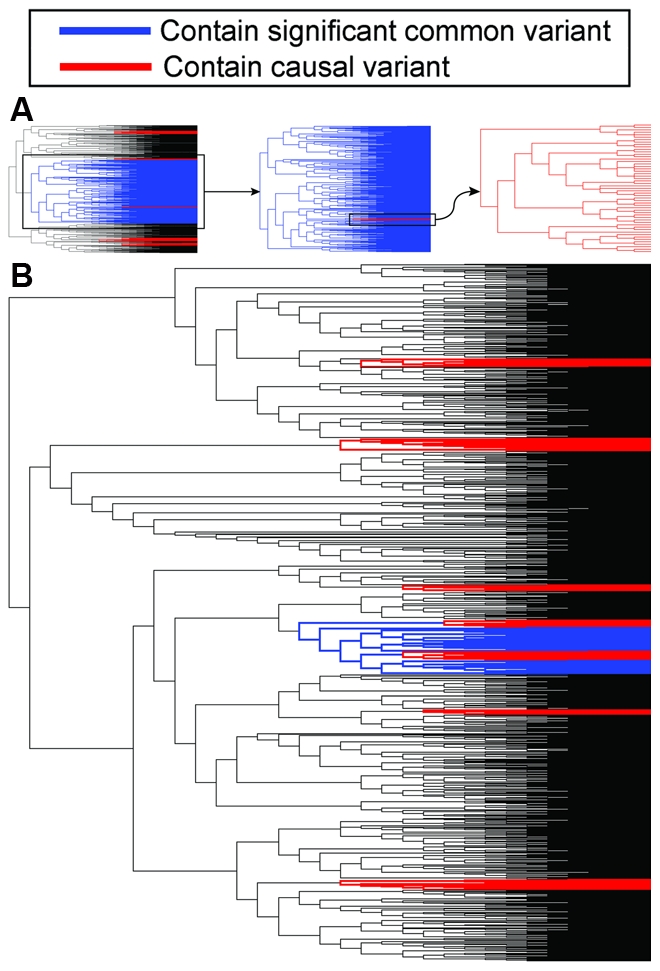
Genome-wide association studies have implicated hundreds of common variants of miniscule effect in diverse traits but a new study suggests that rare variants of much stronger effect may underlie some of these associations. Thus, large-scale sequencing may uncover more definitive leads about disease pathophysiology than the study of common variation has afforded.