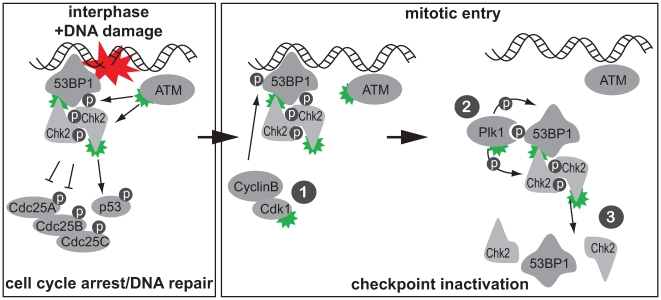
Figure 8. A model for mitotic checkpoint inactivation.
One model for checkpoint inactivation at the G2-M transition. Left panel: DNA lesions promote the formation of protein complexes, including 53BP1 and Chk2, that mediate checkpoint function and promote DNA repair. Green symbols indicate active kinases. Right panel: (1) To terminate the ATM-Chk2 branch of the G2/M checkpoint, CyclinB/Cdk1 phosphorylates DNA damage signaling proteins, including 53BP1. (2) Cdk1 phosphorylation of 53BP1 creates a Plk1 PBD docking site, leading to Plk1 recruitment, phosphorylation of checkpoint components, and inactivation of the Chk2 FHA domain. (3) These combined phosphorylation events by mitotic kinases drive cell cycle reentry and prevent further DNA damage checkpoint activation during mitosis.