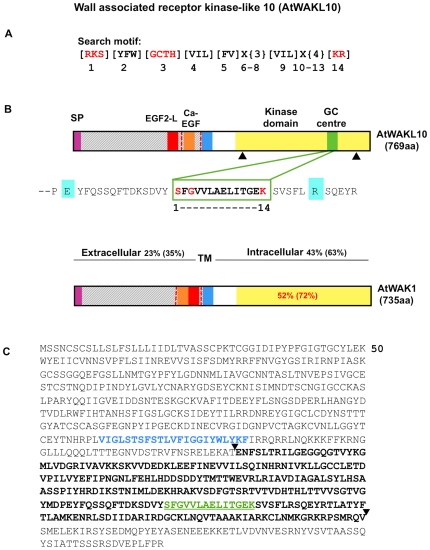
Figure 1. Structural features of the AtWAKL10 protein.
(A) The 14 aa long search motif generated based on conserved and functionally-assigned aa in the catalytic centres of annotated GCs. Amino acid substitutions in the search motif are in square brackets ([ ]); X represents any aa and curly brackets ({ }) define the number of aa. Amino acids in red are functionally assigned residues, [1] hydrogen bonds with the guanine; [3] confers substrate specificity for GTP; [7] binds to the dimer interphase and [14] stabilizes the transition state from GTP to cGMP. (B) Domain organization of AtWAKL10 and AtWAK1 illustrating the location of the predicted signal peptides (SP), extracellular EGF-like domains, TM domains and kinase domains and for AtWAKL10 the GC centre imbedded in the kinase domain. The percentages indicate the determined aa identity and (similarity) between AtWAKL10 and AtWAK1 at the indicated regions. The dashed red vertical lines represent intron locations. The two black triangles demarcate the truncated cytosolic fragment of the AtWAKL10431–700 protein that was expressed as a recombinant. The Arg (R, highlighted in aquamarine) C-terminal of the catalytic centre is a putative metal binding residue and the N-terminal Glu (E, highlighted in aquamarine) is the putative pyrophosphate binding residue. (C) Predicted aa sequence of AtWAKL10. The aa in blue represent the TM domain that separates the extracellular domain from the cytosolic domain. Sequences in bold and demarcated by the two triangles represent the sequence of the recombinant AtWAKL10431–700 protein that was expressed for functional testing. The GC domain is marked in green letters and underlined.