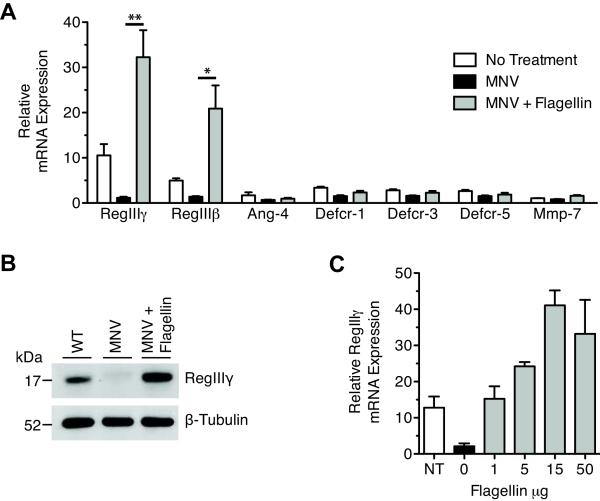
Figure 1.
Flagellin potently induces RegIIIγ and RegIIIβ in antibiotic-treated mice. A, Mice were treated with metronidazole, neomycin and vancomycin (MNV) for 7 days. Starting on day 5 of antibiotic treatment, mice received 15 μg of flagellin per day via intraperitoneal injection for 3 days. Mice were sacrificed 24 hours after the last flagellin injection. Transcriptional expression of RegIIIγ, RegIIIβ, Ang-4, Defcr-1, Defcr-3, Defcr-5, and MMP-7 was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Expression levels were normalized to GAPDH and determined relative to MNV-treated mice. Values are representative of at least two experiments and are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4–9, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction). B. Protein extracts from the distal ileum were analyzed by Western blotting with RegIIIγ-specific antiserum and anti-β-tubulin as a loading control. Shown are representative samples from two experiments (n = 6 for each group). C, On day 7 of MNV treatment, mice received 0, 1, 5, 15, or 50 μg of flagellin intraperitoneally. RegIIIγ mRNA message levels were measured 24 hours later by quantitative real-time PCR and were normalized to GAPDH (n=5 for each group).