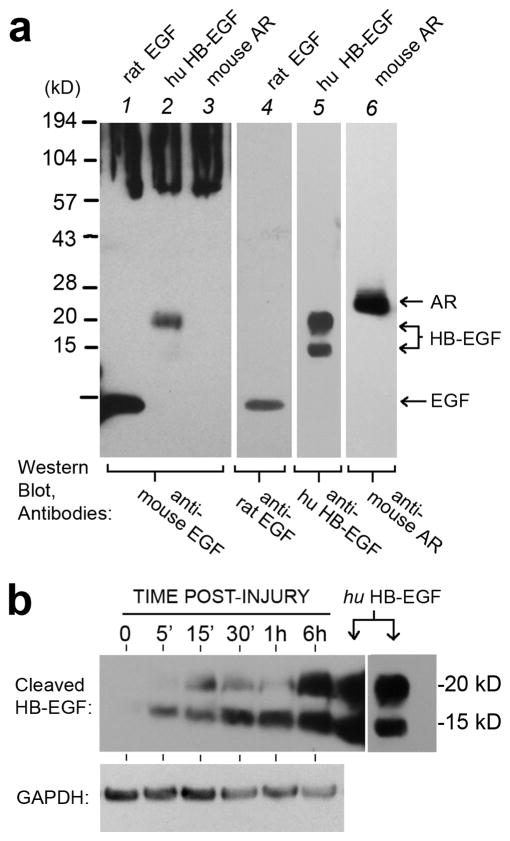
Figure 9. Specificity of a potential HB-EGF neutralizing antibody, and release of cleaved HB- EGF after wounding.
(a), An anti-mouse EGF antibody from Millipore/Upstate (Cat No #06-102) was analyzed for its specificity of binding to the recombinant proteins listed above each lane (all from R&D Systems). Antibodies to rat-EGF (cat no AF3214), human HB-EGF (AF259-NA), or mouse Amphiregulin (AF989) were also from R&D Systems. Note the cross-reactivity of antibody #06-102 with HB-EGF in lane 2. (b), Western blot of REK lift cultures harvested at different times after acute puncture injury, and probed with anti-human HB-EGF (R&D Systems, AF259-NA). Purified recombinant human HB-EGF was used as a protein standard (downward arrows). GAPDH served as a loading control.