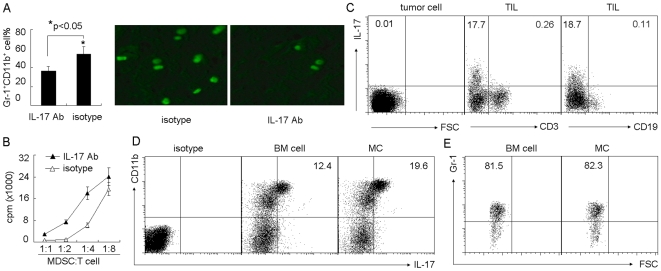
Figure 2. Mast cells regulate MDSCs through IL-17 pathway.
(A) Blockade of IL-17 prevented mast cell-mediated MDSC infiltration to tumor. 5×106 BMMCs were injected into tumor-bearing mice by i.v. injection. IL-17 neutralizing antibody was i.p. injected to the mice 1 h, 2 days and 5 days after BMMCs injection. On day 7, the tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were used to analyze Gr-1+CD11b+ MDSCs by flow cytometry (left). In addition, IL-17 neutralizing antibody was i.p. injected to the mice 24 h and 1 h before BMMCs injection. 2×106 CFSE-labeled MDSCs were injected into the mice two days later. The tumor tissues were surgically excised, and frozen sections were prepared and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy (right). (B) Blockade of IL-17 attenuated mast cell-mediated MDSC suppressive function. BMMCs were injected into tumor-bearing mice. IL-17 neutralizing antibody was i.p. injected to the mice at different time points. On day 7, tumor-infiltrating MDSCs were isolated for the suppression assay. (C) IL-17 was not expressed by H22 tumor cells, T cells or B cells. BMMCs were injected into tumor-bearing mice. Seven days later, tumor cells and TILs were isolated, respectively. The expression of IL-17 was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D and E) Mast cells upregulated the expression of IL-17 by MDSCs. Seven days after BMMCs injection, the isolated TILs were used for IL-17 expression analysis. The data showed the upregulation of IL-17 by CD11b+ cells in BMMC group (D), and most of the gated IL-17+ cells expressed Gr-1 marker (E).