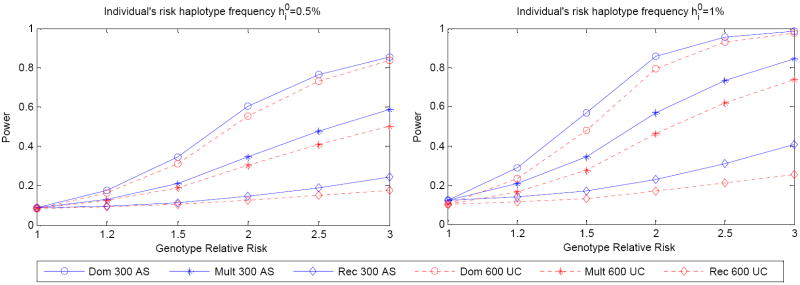
Figure 3.
Theoretical power of co-classifying rare risk haplotypes for the sibpair and unrelated-case designs. Three modes of inheritance were considered: multiplicative f2 = λ f0, ; dominant f2 = f1 =λ f0 and recessive f2 = λ f0, f1 = f0. Haplotype frequencies in the population are known. 300 affected sibpairs and 600 unrelated cases were used. The cumulative risk haplotype frequency is 10%. Left panel: individual risk haplotype frequency is 0.5%. Right panel: individual risk haplotype frequency is 1.0%.