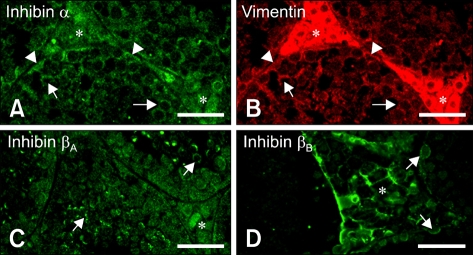
Fig. 3.
Immunofluorescent localization of inhibin α, βA, and βB isotypes in mouse testis at postnatal days 48. (A and B) Double-immunofluorescent staining in the same section showed the co-localization of inhibin α with vimentin in cell bodies of Sertoli cells (arrowheads), the cytoplasmic process of Sertoli cells (arrows) and in interstitial spaces (asterisks). (C) Immunofluorescent localization of the inhibin βA subunit was observed in the cell membrane of some spermatogenic cells (arrows) as well as in the interstitial cells (asterisk). (D) Immunofluorescent localization of the inhibin βB subunit was observed mainly in cell membranes of interstitial cells (asterisk) as well as in some spermatogonia (arrows). Scale bars = 30 µm.