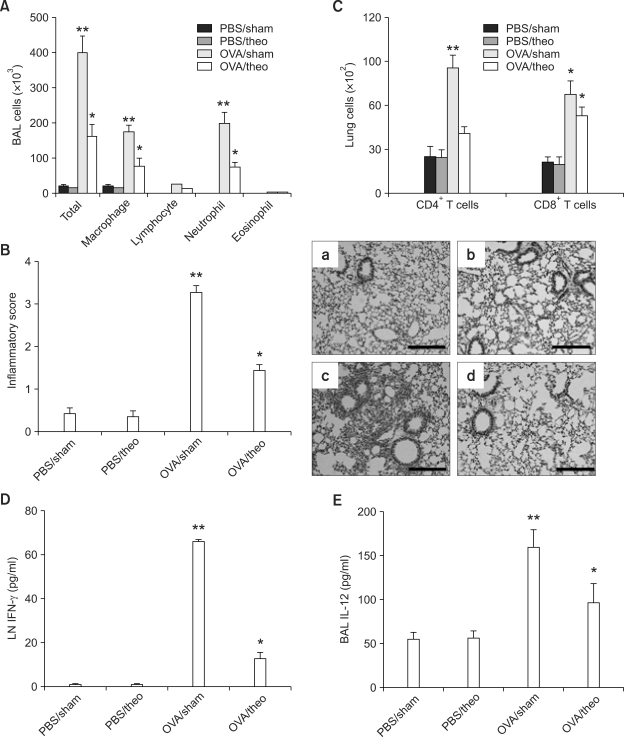
Figure 1.
Theophylline shows therapeutic effects on neutrophilic inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide-containing allergens. Evaluation (n = 5 each group) was performed after allergen challenge. PBS, mice sensitized with ovalbumin and then challenged with PBS; OVA, mice sensitized with ovalbumin + lipopolysaccharide and then challenged with ovalbumin; *P < 0.05 compared to the PBS sensitized groups; **P < 0.05 compared to other groups. (A) BAL cellularity 48 h after the final allergen challenge. (B) Lung inflammatory scores based on histology (left panel) and representative lung histological findings 48 h after the final allergen challenge. a: PBS_sham; b: PBS_theo; c: OVA_sham; d: OVA_theo (H&E stain, × 200). Magnification bar = 200 µm. (C) Number of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in lung tissues 6 h after allergen challenge on day 21. (D) IFN-γ levels in supernatants prepared from T-cells collected 6 h after anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 stimulation. T-cells were isolated from lung draining lymph nodes (LNs) 6 h after allergen challenge on day 21. (E) BAL IL-12p40 levels 48 h after the final allergen challenge.