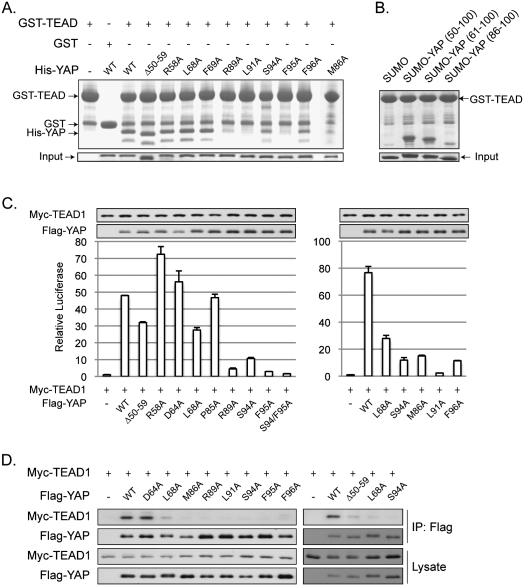
Figure 3.
Effect of YAP mutations on YAP–TEAD-binding affinity. (A) In vitro pull-down assay. His-tagged YAP (50–171) and mutants were tested in a GST pull-down assay using GST-TEAD (194–411) immobilized on glutathione resin. Pull-down products were analyzed by Tricine-SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (B) In vitro GST-TEAD pull-down of different YAP fragments. Three YAP fragments, as indicated, were expressed and purified as SUMO fusions. In vitro pull-down was performed as described in A and was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (C) CTGF reporter assay. Indicated plasmids were cotransfected with a CTGF reporter and a CMV–β-gal construct into 293T cells. Luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. YAP and TEAD expression levels were determined by Western blot with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies, respectively. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation. Flag-YAP wild type or mutants were cotransfected with Myc-TEAD1 wild type into HEK293 cells. Flag-YAP was immunoprecipitated, and coimmunoprecipitated TEAD1 was determined by anti-Myc Western blot.