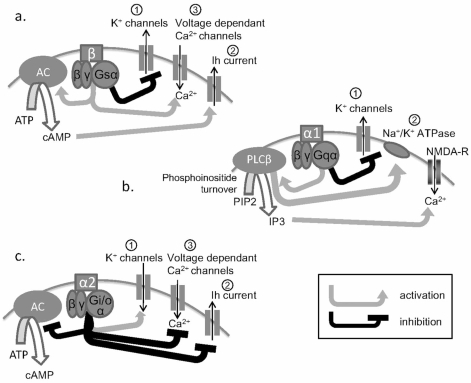
Fig. (1). Schematic representations of the action of adrenoceptors that induce intrinsic plasticity.
a. β-adrenoceptor activation generally induces depolarization of postsynaptic neurons with an increase of input resistance. It reduces K+ currents (1) and facilitates Ih current via cAMP pathway (2) and the entry of Ca2+ (3).
b. α1-adrenoceptors can also induce depolarization of neurons with an increase of input resistance. They reduce K+ currents (1) and act on Ca2+ entry via the activation of phosphoinositide turnover (2).
c. α2-adrenoceptors generally induce hyperpolarization coupled to an increase or decrease of input resistance via blockade of Ih current (2) or opening of K+ channels (1) respectively. They also inhibit Ca2+ channels (3).
AC, adenylate cyclase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ca2+, calcium; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DAG, diacylglyrerol; Ih, hyperpolarization-activated currents; IP3, inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate; K+, potassium; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol biphosphate; PLCβ, phospholipase Cβ.