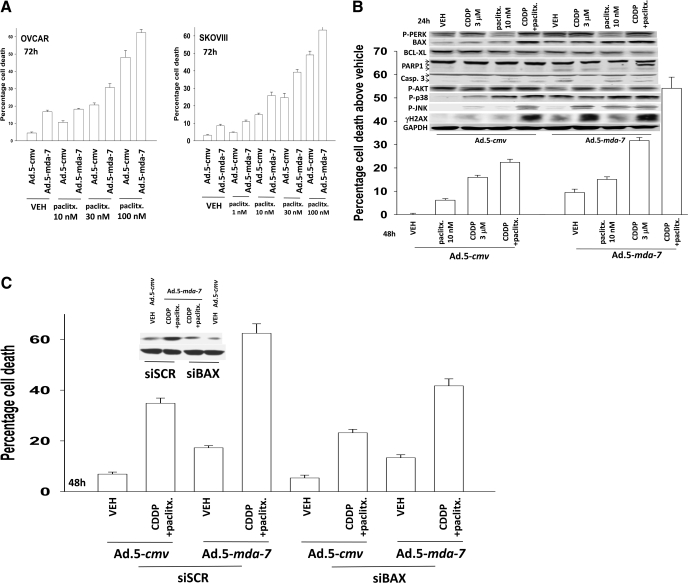
Fig. 5.
Paclitaxel enhances the toxicity of Ad.5-mda-7 + cisplatin in a greater than additive fashion. A, OVCAR and SKOVIII cells were infected with Ad.5-cmv or Ad.5-mda-7 at an m.o.i. of 80. Twenty-four hours after infection, as indicated, cells were treated with paclitaxel (paclitx., 0–100 nM). Cells were isolated 48 h after infection, and the loss of cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assays in triplicate (± S.E.M., n = 3). B, OVCAR cells were infected with Ad.5-cmv or Ad.5-mda-7 at an m.o.i. of 80. Twenty-four hours after infection, as indicated, cells were treated with paclitaxel (paclitx., 10 nM) and/or cisplatin (CDDP, 3 μM). Cells were isolated 48 h after infection, and the loss of cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assays in triplicate (± S.E.M., n = 3). Top inset, cells were isolated 24 h after virus infection and processed for SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting against the indicated proteins to determine expression/phosphorylation (n = 2). C, OVCAR cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siSCR) or an siRNA to knock down BAX expression and 24 h later were infected with Ad.5-cmv or Ad.5-mda-7 at an m.o.i. of 80. Twenty-four hours after infection, as indicated, cells were treated with paclitaxel (paclitx., 10 nM) and cisplatin (CDDP, 3 μM). Cells were isolated 48 h after infection, and the loss of cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assays in triplicate (± S.E.M., n = 3).