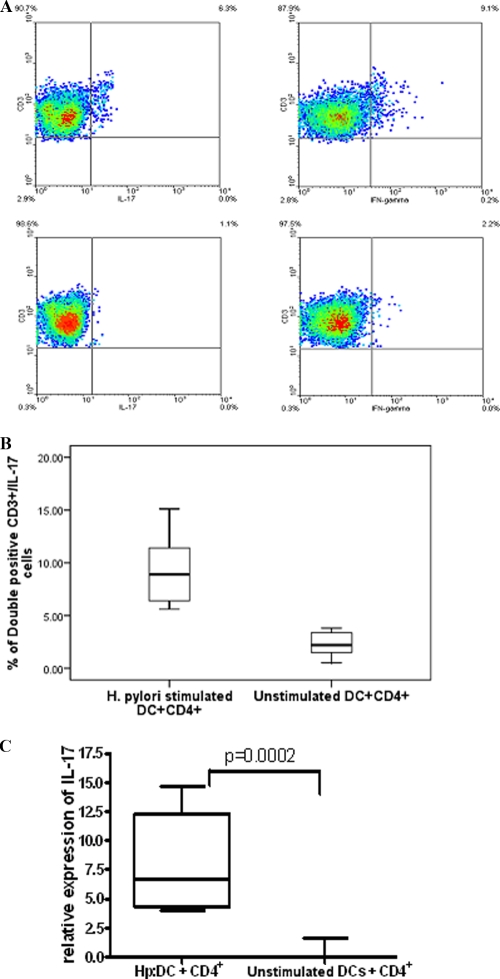
FIG. 5.
H. pylori induces IL-17 expression from CD4+ T cells. (A) ICS of CD4+ T cells following coculture with H. pylori-stimulated DCs. At 5 days after coculture, CD4+ T lymphocytes in the presence of H. pylori-treated DCs were restimulated with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of monensin. Cells were stained for surface markers using anti-CD3-PE and for intracellular cytokines using IL-17-Alexa Fluor 488 (top left) and IFN-γ-APC (top right). Isotype controls used were IgG-Alexa Fluor 488 and IgG-APC (bottom left and right, respectively). (B) Comparison of cumulative data for ICS from CD4+ T cells stimulated with untreated or H. pylori-treated DCs (P = 0.001) (n = 7). (C) IL-17 expression from cocultures of H. pylori-treated DCs or unstimulated DCs with CD4+ T cells assessed by real-time PCR (cumulative data from 7 experiments) shows a significant increase in numbers of H. pylori-treated DCs compared to untreated DCs (P = 0.0002). The relative expression level of IL-17 is expressed as −δδCT. (Hp:DC, H. pylori-stimulated DCs).