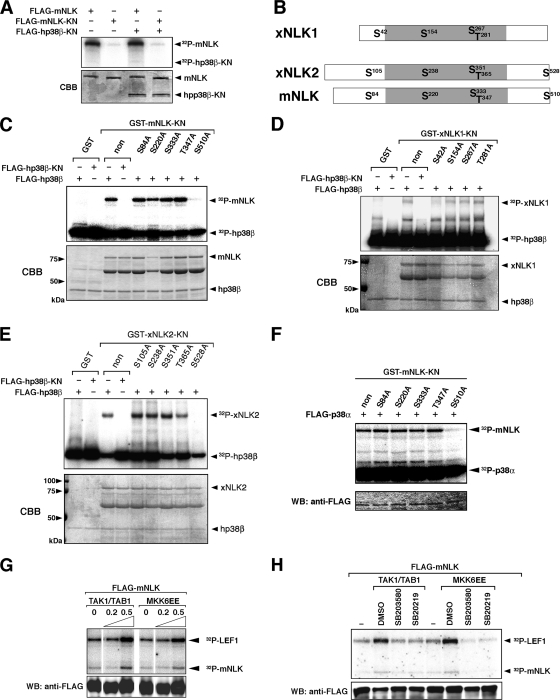
FIG. 2.
p38β phosphorylates a specific site in NLK. (A) Phosphorylation of p38 by NLK. 293 cells were transfected with Flag-tagged genes and a constitutively active form of MKK6 (MKK6EE). Immunoprecipitates obtained with an anti-FLAG antibody were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP. (B) Schematic of NLK genes. The putative p38 phosphorylation motifs are indicated as S and T. The kinase domain is shaded. (C to E) Phosphorylation of NLK by p38β. 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged hp38β or hp38β-KN, together with MKK6EE. Immunoprecipitates obtained with an anti-FLAG antibody were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and bacterially expressed mNLK-KN and its mutants (C), xNLK1-KN and its mutants (D), or xNLK2-KN and its mutants (E). Phosphorylation and Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of each protein are indicated by arrowheads. (F) Phosphorylation of NLK by p38α. 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged p38α. Immunoprecipitates obtained with an anti-FLAG antibody were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and bacterially expressed mNLK-KN and its mutants. The phosphorylation of mNLK and p38α is indicated by arrowheads. (G and H) COS1 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged mNLK, together with TAK1/TAB1 or MKK6EE. Immunoprecipitates obtained with an anti-FLAG antibody were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and bacterially expressed LEF1 as a substrate. (G) Enhancement of phosphorylation by TAK1/TAB1 or MKK6 (MKK6EE). Numbers indicate amounts of transfected genes (μg). (H) Preincubation with SB203580 and SB20219, specific inhibitors of p38 activity, reduced phosphorylation of LEF1.