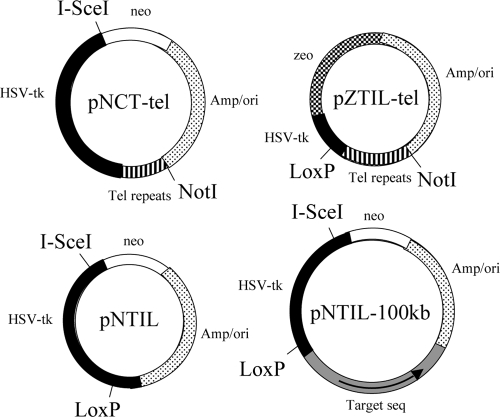
FIG. 1.
The structure of plasmids used in this study. pNCT-tel contains a Neo gene, HSV-tk gene, and telomeric repeat sequences. pNCT-tel also contains an I-SceI recognition site, which is located between the Neo and HSV-tk genes. pNCT-tel was linearized with NotI prior to transfection. Linearization places the telomeric repeat sequences on one end to seed the formation of a new telomere following integration. pNTIL contains the Neo gene and an HSV-tk gene that contains a LoxP site in its 3′ untranslated region. pNTIL also contains an I-SceI recognition site, which is located at the 5′ end of the coding region of HSV-tk. pZTIL-tel contains a Zeo gene and a fragment of the noncoding region of the HSV-tk gene containing a LoxP site. pZTIL-tel was also linearized with NotI prior to transfection, both to facilitate targeted integration into the pNCT-tel plasmid and to place the telomeric repeat sequences on one end to seed the formation of a new telomere. pNTIL-100kb is similar to pNTIL, except that it contains a 4.5-kb fragment of the magmus gene (Target seq) for targeting to a site 100 kb from the telomere containing the pZTIL-tel plasmid. The magmus gene fragment is oriented with its distal end closest to the ampicillin gene (arrow).